[ad_1]
Today is the world bone marrow donor day. And Brazil won the rank of third largest bone marrow donor bank in the world, with more than five million people registered in the Redome (National Bone Marrow Donor Registry).
However, according to a report released by the ABTO (Brazilian Association of Organ Transplantation) between January and June of that year, the number of bone marrow transplants performed in the country decreased by almost 20% compared to the same period last year. In addition, since the start of the coronavirus pandemic, the number of organ donors has dropped 34% and the number of organ transplants has dropped more than 40%.
However, the expectation is that there will be an increase in the number of donors this year. “For this to happen, it is essential to inform the population about the safe processes and flows within blood centers and hospitals, and to raise awareness that bone marrow donation is a gesture of solidarity that can save lives,” says Bruno Ferrari, oncologist clinician, founder and president of the Board of Directors of Grupo Oncoclínicas.
In addition to the decline in donations due to the pandemic, patients must cross another barrier: finding a compatible donor. Among non-relatives, the probability of compatibility is 1 in 500 thousand people. Between siblings, the probability is 30%.
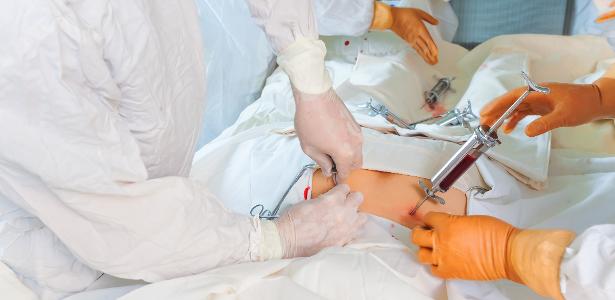
Transplantation is a low-risk procedure
Bone marrow donation is a low-risk procedure and, depending on some factors, it can be performed with peripheral blood through a process called cytopheresis or by collecting bone marrow from the crests of the iliac bones, under general anesthesia. “It is a process that is carried out in a surgical center that requires 24-hour hospitalization,” explains the hematologist from the Oncoclinical Group, Wellington Azevedo.
How to be a donor?
To apply, you must register as a voluntary bone marrow donor at one of 106 blood centers located in every state in the country. Here are some requirements:
- Be between 18 and 60 years old;
- Be in good general health;
- Not present neoplastic (cancer), hematological (blood) or immune system disease.
After completing a form with personal data, only 10 ml of blood is drawn from the donor candidate to perform the HLA (histocompatibility) test, which is crossed with the data of patients awaiting transplantation.
Finally, it is important that candidates always keep their information, such as telephone number, email and address, up to date, so that when there is compatibility, they can be contacted.