[ad_1]
by César Soares and Josélia Pegorim
New eruption of Anak Krakatoa volcano
The Anak Krakatau (son of Krakatoa, in Javanese translation) volcano, located on an island between Java and Sumatra, in Indonesia, returned in outbreak on Friday April 10, 2020. According to the news agencies, there were no victims, but as of Saturday morning, the volcano continued to erupt.
This volcano is the son of the known. Krakatoa Volcano, which erupted violently in 1883. The plume of smoke from this volcano persisted for a long time in the atmosphere causing global atmospheric cooling period.
According to information from the Icelandic weather service, around 8,000 earthquakes have been recorded since the end of January. The magma elevations came 10 cm ago, warning that volcanic activity may increase further.
That way, Scientists fear that during increased seismic activity in the region, volcanic activity will span decades.. There is a risk that lava will flow into the city of Grindavík, impacting and endangering the lives of several people.
Discover the 10 largest deserts in the world.
A bit of Krakatoa’s family history
Once there was an island called Krakatoa, where the Krakatoa volcano was. But on August 26, 1883, the volcano violently erupted and the island disappeared from the map.
This 1883 eruption was the largest in the Krakatoa volcano. It was the highest number of deaths associated with volcanic activity, with approximately 36,000 deaths.
Over time, a crater began to emerge from the crater. rock formation called Anak Krakatoa, the son of Krakatoa.
Anak Krakatoa volcano arose from what was left of the great eruption of Krakatoa volcano, the “father”. The last time Anak Krakatoa exploded was in 2018, which caused a tsunami and killed 437 people. Although the eruption occurred in December 2018, the volcano already showed signs of activity six months earlier, starting in June.

Curiosities about the Anak Krakatoa volcano
Pyrocumulus clouds
During the volcanic eruption process, a very specific type of cloud occurs, which is the pyrocumulus, or cloud of fire.
This type of cloudiness has intense turbulence, which in turn causes strong gusts of wind on the surface and even lightning can be observed. This is because the magma rock particles are also released into the atmosphere in the form of ash. These The rocks hit each other and end up generating electrical charges that generate lightning.
Volcanic aerosols
Volcanic spray is one of three types that directly affect Earth’s climate. The other two are the desert and human action. Here, we will focus on aerosols from volcanoes and their direct action in the atmosphere.
Some Volcanic eruptions they are so strong that they can spewing aerosol particles in very high layers of the atmosphere, as in the stratosphere that is between 15 km and 50 km. The dominant composition in this type of aerosol is sulfur dioxide (SOtwo) which can be converted into drops of sulfuric acid (HtwoSW4 4) When in contact with water in the atmosphere, this concentration can last for months after the eruption.
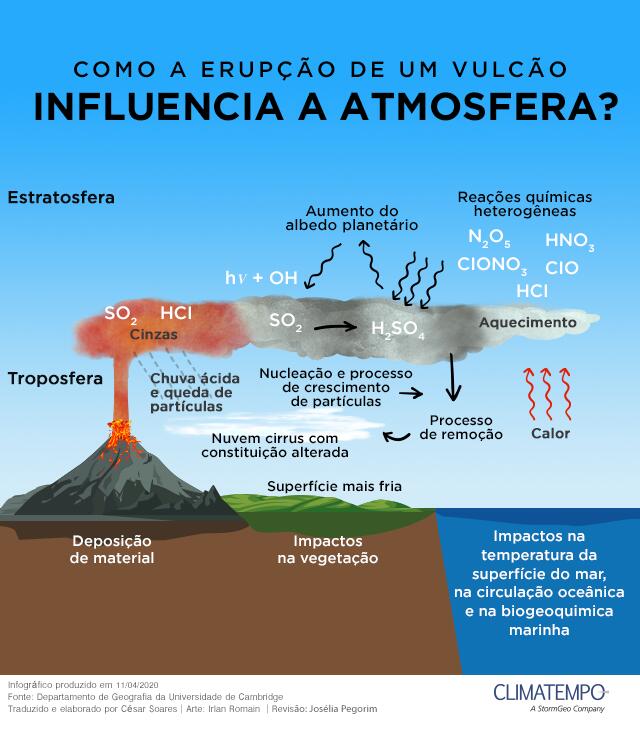
How the remains of a volcanic eruption interfere with the atmosphere
Stratospheric winds transport these aerosols practically throughout the world, which, once formed, can circulate in the atmosphere for up to two years..
Volcanic aerosols reflect sunlight, which reduces the energy that reaches the Earth’s surface. Therefore, the local temperature tends to decrease, as there is a decrease in sunlight.
[ad_2]