
[ad_1]
As Karolis explains, when you tried to register a car through a government electronic gate, you were charged a registration fee (pollution). According to the reader, according to the laws of the Republic of Lithuania and the parameters provided by the manufacturer, such a tax should not be applied to this car.
The controversial car was manufactured in 2011 by Volkswagen, with a displacement of 1598 cubic centimeters, 77 kW and 1.6 liters. Diesel engine. According to Karolis, this engine is marked with the CAYC code in the Volkswagen Group.
The technical passport did not contain CO2 emissions or other mandatory data …
It is true that the car’s CO2 emissions did not contain CO2 emissions or other data necessary to determine CO2 emissions in the simplest way, so one of the formulas used was used in the calculation.
However, Carol, driving in 2011. According to Passat, in this case SE Regitra applies illegal taxes “without knowing” the parameters of the car.
“It’s strange, because I think that when an institution like this charges for cars, there must be clear technical parameters. Furthermore, such a motor vehicle is not the only one in Lithuania (different manufacturers with the same type of engine). Either people are deceived, or some people are subject to these requirements and others are not, which would also be illegal ”, the reader considered.
According to him, a registration fee of € 60 was applied to the car.
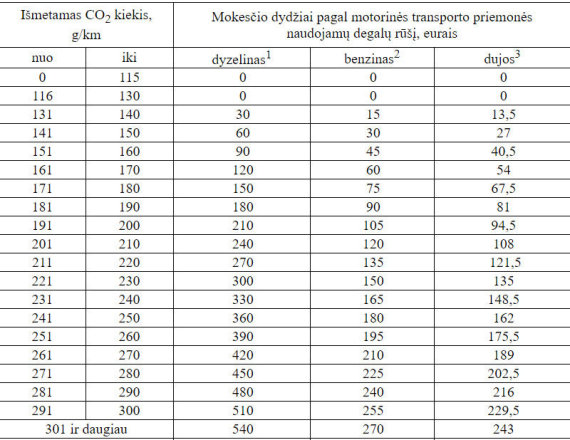
Motor Vehicle Registration Tax Rates
How is CO2 determined?
Regitra’s communication specialist, Emilija Bardauskienė, explains that Regitra administers the registration tax in accordance with the Law on Motor Vehicle Registration Tax, which came into effect in July.
Therefore, the law establishes four methods for determining CO2, on the basis of which only the amount of the registration tax can be calculated. They are applied in the following order.
“First of all, the indicator value is used from official documents and certificates that provide information about a specific car to be registered, that is, the origin of the car (registration certificate) or approval documents (eg. , Certificate of Expertise, Certificate of Conformity (CoC)). Excerpts from the Register of Road Vehicles can also be used. Based on July data, this method is the most common, accounting for about 67 percent. in all cases ”, says E.Bardauskienė.
Not all sources are reliable
The specialist emphasizes that, for example, general vehicle data provided on the websites of car manufacturers or their representatives are not considered the sources from which CO2 can be determined.
“The second situation is that if CO2 emissions are not specified in these documents, the registry looks for equivalent vehicles and uses their CO2 value. In this case, it is important to note that the registered car and the other vehicle in the register must comply with the European Union homologation, that is, the type, variant and version must be the same and marked with separate codes. They can be found in box D.2 of the registration certificate.

Regitra photo / Car registration certificate
Thus, when automatically calculating the toll, the Registry of Highway Vehicles looks for another vehicle with the same codes, which is then considered identical in terms of technical parameters. The type, variant and version include more information about the car than, for example, the make, model or engine power, ”says E.Bardauskienė.
According to the European Union directive, vehicles must match all parameters, such as not only the model, engine, but also the type of fuel, chassis, number of cylinders and their arrangement, drive axles, etc.
“If there are no equivalent vehicles in the register and / or there is no such sign to identify an identical car, the third method is used and the amount of CO2 is calculated according to the formulas provided by law. This requires the technical data of the vehicle in the original or homologation documents: mass of the motor vehicle in running order (kg), maximum engine power of the motor vehicle (kW), type of gearbox, type of fuel or power source. Depending on the type of fuel in the car, not all data may be used in the calculation.
The fourth method: if it is not possible to calculate the CO2 content according to the formulas by inputting the technical data of a specific car, then the data of equivalent vehicles is used, that is, the formulas use the above-mentioned technical data of equivalent cars ”, Explains E.Bardauskienė.
Well, if it is not possible to apply any of the four methods for CO2 determination mentioned above, then a technical examination must be performed and a technical examination certificate must be submitted for the determination of the actual data. According to E.Bardauskienė, these cases are not common.

Photo from 123RF.com/Exhaust pipe
Engine parameters alone are not enough
According to E.Bardauskienė, speaking of the Karolis situation, during the registration, the CO2 content of his car in the electronic space was automatically determined by applying one of the aforementioned methods.
“From the situation described, it seems that it was not possible to apply the first two methods. In other words, the emissions were not indicated in the available documents of origin or approval of the car, which were presented at the time of the first registration, nor was an equivalent vehicle registered in the registry according to the approval of the European Union, is say, type, variant, version.
As already mentioned, for example, engine parameters alone are not sufficient to assess the equivalence of vehicles. Thus, for this reason, the third method was applied and the CO2 content was calculated according to the formula established by law ”, says E. Bardauskienė.
And when registering a car online, the methods for determining CO2 and its order of priority remain the same.
[ad_2]