
[ad_1]
After a year, we will enjoy the delicious gifts of others, and the beautiful landscaped garden will bring aesthetic admiration. In order for our work to be fruitful and uneven, let’s remember a few tips.
Choosing a place for the garden
Higher ground areas are the most suitable: they are not too humid, during winter and frost cold air travels to lower places and fruit trees grow healthier and more productive. On the plains, conditions are worse, especially if heavier soils predominate. Fruit trees and fruit bushes should not be planted in ravines. They are usually too wet and too cold. In the cold winter, the plants will freeze or freeze, in the spring the frosts will bloom, the plants will get sick. The most demanding are peaches, apricots, cherries and cherries. It is advisable to plant peaches and apricots only in sunny places with a warmer microclimate, protected from strong winds.
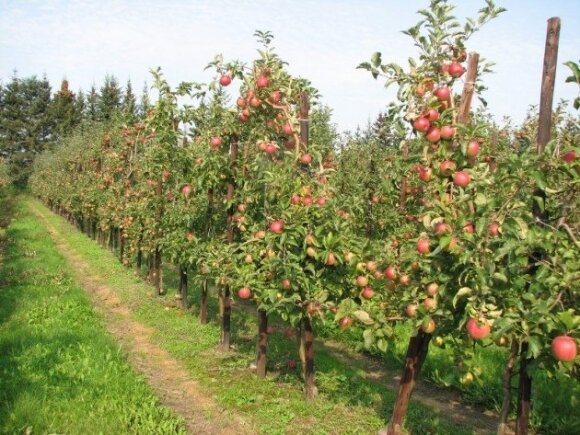

Garden planting
© Personal album
Soil preparation
Very good when perennial weeds are pulled up in the garden area, the soil is fertilized, plowed and cultivated before planting. If you have to plant in a poorer location, like a lawn, you have to prepare the soil. Initially, the grass is removed and a slightly larger planting pit is dug (diameter – 80 cm, depth – 40 cm). Neutralized peat substrate or compost can be added to the soil. It is advisable to fertilize less fertile soils with mineral fertilizers. 100-150 g of superphosphate and 50-100 g of potassium sulfate should be added to a planting pit. Complex fertilizers with low nitrogen content (up to 5%) and high phosphorus and potassium content, such as NPK 5-15-20, are also suitable. Nitrogen fertilization is required a little later, about a month after sowing. In the first year, plant a handful of ammonium nitrate in the root zone of the plant.
Blueberry cultivation
Blueberries grow well and do well only in acidic soils. If the soil is neutral or alkaline, the planting site should be prepared. Rather large pits (about 1 m wide and 0.5 m deep) are dug, filled with a specially prepared substrate for blueberries from peat and acid tree bark (pH about 4.0). A 5-10 cm layer of coarse sand or gravel can be added to the bottom. Planting holes must be filled with substrate in advance so that it is well contracted. For spring-planted blueberries, the planting site is best prepared in the fall to allow the substrate to collapse.
Planting distances
Spaces should be left between fruit trees and fruit bushes in the garden, depending on the type, variety, pattern, and method of growing the plants in the garden. Growing apples, pears, and cherries are planted in rows every 4–5 m, medium-sized every 3–3.5 m, semi-dwarfs every 1.5–2.5 m, dwarfs every 1–2 m. Depending on the variety, a gap of 2-3 m is left between cherries and plums, raspberries are planted at a distance of 0.3-0.5 m, blueberries, gooseberries to be picked by hand, and gooseberries every 1-1.5 m. The spacing between the rows should be approximately 1.3-1.5 times the expected height of the fruit trees.

Garden planting
© Personal album
Planting time
In spring, it is better to plant fruit trees and fruit bushes before the start of vegetation. Sowing can be done after leaving the field and after the soil has dried. Planting in too humid soils damages its structure and damages the growing conditions of the roots. In favorable weather conditions, fruit trees and fruit shrubs can be planted in lighter soils in the second half of March and throughout the month of April. Later, when the seedlings are planted, the plants have a harder time healing and suffer more from the droughts that have occurred frequently in recent years. Seedlings sold in pots can almost always be planted, except during winter when the ground is frozen.
Getting ready to plant
Before planting, the roots of the plants must be protected so that they do not dry out. It is advisable to moisten them and put them in a wide polyethylene bag or wrap them in polyethylene film. Seedlings that have begun to explode must be handled with great care. If imported plants cannot be planted immediately, they must be dug up. A larger hole is dug to accommodate the roots of the plant and buried in the ground. It is better to dry where the shade falls – the plants will not get hot in the sun, they will wake up more slowly from forced rest.
Planting
The roots of the fruit trees to be planted in the hole should be spread out as evenly as possible in all directions. Broken and overly long roots should be pruned so they don’t bend. The seedling is placed in a pile made at the bottom of the hole. After pouring a layer of soil, they are covered so that they better fit the roots. After planting, tap. The bigger the well is dug, the more water is needed. When the water is absorbed, a thin layer of drier soil is sprinkled on top.
Seedlings of apples, pears, cherries and cherries with seed rootstocks are planted up to the root neck. Plums grafted onto seedlings (Caucasus) should be planted slightly deeper than the graft site. Trees planted this way produce fewer rootstock cuttings. Fruit trees with vegetative rootstocks (dwarf, semi-dwarf and medium) are planted so deep that the graft site remains above the ground. The longer the rootstock is left above ground, the lower the trees grow. Gooseberries and currants are planted deeper – the root neck should be 6-8 cm below the ground. When planted this way, more lush fruit bushes form, are more durable, and more replacement stems are grown. The raspberry root collar should be at ground level, and only in light soils it can be planted about 5 cm deep.
Shredded
Mulching creates more favorable conditions for moisture, fewer weeds germinate. Peat is better for this. Mulch with a radius of about 50 cm around the trunk, the thickness of the mulch should be about 5-10 cm.
Pruning
When buying annual grafts without a crown (lateral shoots), the apex above the bud should be shortened to a height of about 90 cm. When the lateral branches of the seedlings are too close to the ground or have only simple lateral shoots, all lateral formations are removed and the apex is cut at that height (Figure 1).

Garden planting
© Personal album
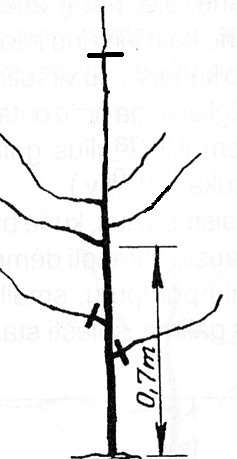
If the cup seedlings are 70-90 cm tall, their apex shortens about 50-60 cm above the highest lateral shoot (Figure 2). Very long side shoots are also slightly shortened. On the first floor of the crown, 3-5 branches are needed for fruit trees. If there are more side shoots, their excess is removed.

Garden planting
© Personal album
If the side shoots grow upwards, it is advisable to bend them horizontally and tie them with a rope to the bottom of the trunk or to the support post. When the branches acquire the desired direction of growth, the cord is untied. Stronger upright growing shoots that compete with the crown should be removed (Figure 3) so that the fruit tree has only one stem and no competing branches are broken.
Garden planting
© Personal album
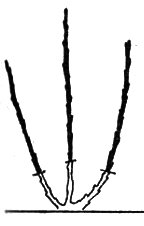
Currant and gooseberry shoots are shortened, leaving 2-3 buds above the ground (Figure 4). From them will grow strong shoots, the fruit bush will be more lush. If there are many sprouts, the part can be left whole.
Garden planting
© Personal album
It is strictly forbidden to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, it is necessary to cite DELFI as the source.
[ad_2]