
[ad_1]
The world’s largest free trade zone will be launched, covering 30% of the world economy. It is a “Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (RCEP)” in which Korea, China, Japan, Australia, New Zealand and 10 ASEAN countries (Vietnam, Thailand, Singapore, Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, etc.) participate. Through RCEP, the first Free Trade Agreement (FTA) was signed with Japan.
The gross domestic product (GDP) of the 15 countries under RCEP is $ 2.63 trillion in 2019 (about 9,000 trillion won). It represents 30% of the world. These countries represent 28.7% of world trade and 29.9% of the population. It is more than twice the size of the North American Free Trade Agreement (USMCA) and the Comprehensive and Progressive Trans-Pacific Economic Partnership Agreement (CPTPP) (in terms of trade).
Governments of RCEP participating countries, including Korea, signed on the 15th, but parliamentary ratification procedures continue. RCEP comes into effect only when 6 out of 10 ASEAN countries and 3 out of 5 countries have ratified it. Of course, validity is limited to countries that have been ratified.

President Moon Jae-in listens to Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyen Xuan Phuc’s closing remarks at the signing ceremony of the ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)’, the world’s largest free trade agreement (FTA) ever concluded at the Blue House on the 15th. Yunhap news
‘Update’ of the existing bilateral FTA
RCEP is a ‘mega FTA’ that was born after eight years of tug of war after negotiations began in 2012. However, it is not a huge variable that can change the entire import and export market from Korea’s perspective. It is because they already have a one-to-one FTA with most of the participating RCEP countries. It may be significant that the existing FTA has been “updated.”
With the launch of the RCEP, the level of tariff elimination for each product item in 10 ASEAN countries will increase from 79.1 to 89.4% today to 91.9 to 94.5%. This means that between 91.9% and 94.5% of tariffs among commercial items will be phased out. This is the point where domestic companies with production bases in ASEAN countries can benefit.
It has decided to phase out tariffs on freight cars, passenger cars, car engines and auto parts, which amount to 10-40% per country. Tariffs such as steel products (up to 5%), steel pipes (20%), and plated steel sheets (10%) are also subject to suppression. In some countries, tariffs on refrigerators, washing machines and air conditioners, which currently stand at 25-30%, are also expected to be eliminated.
The elimination of tariffs with China, Australia and New Zealand has already been set at a bilateral FTA level of more than 90%.

President Moon Jae-in is preparing for the meeting by attending the second Korea-Mekong video summit held in the main building of the Blue House on the 13th. Photo reporters from the Blue House
First FTA with Japan … Challenges of domestic materials, parts and equipment
Korea and Japan signed an FTA for the first time through RCEP. Both countries have decided to abolish the tariff on 83% of the articles. However, Korea excluded sensitive items such as automobiles and machinery from the concession to Japan. For items to be opened, the fees will be dropped for a long period of 10-20 years, or the fees will be phased out after keeping the current fees for a specified period of time (non-linear abolition).
Kim Young-man, head of the Products Division of the Free Trade Agreement at the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy, said: “The focus (in the negotiations) with Japan is to protect the market and increase the burden of purchasing goods. intermediates in Japan by comprehensively considering the level of openness, industrial competitiveness, and countermeasures against Japanese export regulations. “I put it.”
With the launch of RCEP, the prices of imported tropical fruits and beer from ASEAN and elsewhere are expected to decline in the future. The tariff (30 ~ 45%) on durian, papaya, guava and mango will be eliminated in 10 years. The tariff (30%) on beer is also eliminated for 15-20 years. Although not immediately, it does mean that prices for tropical fruits and beer that are distributed in Korea may be cheaper.
However, items such as rice, garlic, onion and pepper, which are key sensitive agricultural products, were excluded from the concession. Sensitive items with high imports such as shrimp, squid, sea bream and defense were also withdrawn from the concession.
Through the RCEP, a unified rule of origin has been created in 15 countries and the certification and reporting process is also simplified. The foundations have also been laid to solve problems such as illegal copying of Korean Wave content. This is because protection rules were created for general intellectual property rights, such as copyrights, patents, trademarks and designs, and remedies such as civil and criminal infringement proceedings were created.
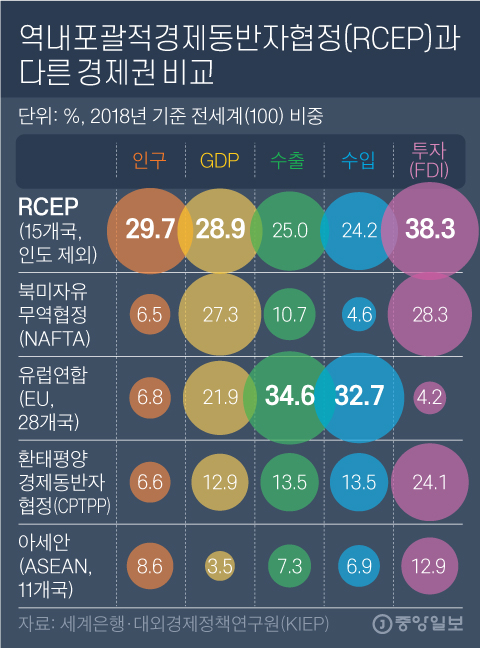
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (RCEP) compared to other economies. Graphic = Reporter Kim Young-ok [email protected]
Low level of agreement, limited lack of delivery
The world’s largest free trade zone was created with RCEP, but there are limitations. The level of openness by item is lower than that of other LACs focused on developed countries, since many developing countries participate, which have lower manufacturing competitiveness compared to advanced countries. The period of tariff reduction is also long, from 10 to 20 years. It is not a structure that immediately affects the domestic industry.
Park Tae-ho, director of the Gwangjang International Trade Institute (formerly director of the Kwangjang International Trade Center), said: “It is significant that 15 countries have agreed and signed a sign in a situation where the uncertainty in the environment Global trade is increasing, but there are limitations. ” “Pacific Pacific Economic Partnership (TPP) Agreement” Compared to CPTPP and liberalization, the agreement was made at a very low level in international standards, and its meaning has faded when India was omitted. ”
India was present at the beginning of the RCEP negotiations, but declared itself absent from the process. India, which does not have high manufacturing competitiveness compared to the size of the market, was not satisfied with the opening of trade in the early stages of the RCEP. It is an analysis that the expansion of the trade deficit with China was cited as a reason for the non-participation. As the political and diplomatic conflict with China, which spearheaded the RCEP, deepened, India ultimately decided to withdraw.
Leaders who attended the RCEP signing ceremony that day issued a joint statement claiming it is “open to India,” but India’s participation is still uncertain.
Biden is inevitable to compete with CPTPP
With the advent of the RCEP ‘Mega FTA’, the international trade landscape has become more complex. This is because there is unavoidable competition with the CPTPP, which has gained momentum for the resurgence of Joe Biden’s US presidential election.
The roots of the CPTPP are the TPP, led by the Barack Obama administration and the Democratic Party. When President Donald Trump decided to withdraw from the US TPP, it transformed into a Japan-led CPTPP.
Therefore, it is analyzed that Biden becomes the owner of the White House and that the participation of the United States in the CPTPP is a matter of time. With the launch of RCEP, a China-led economic community, the return to CPTPP is anticipated to rush to prove this.
The Korean government’s concerns are also deepening. Currently, Korea has not participated in the CPTPP and has not disclosed a clear position on it. “We are analyzing the general impact of the US presidential elections and looking at various scenarios, and we are reviewing what strategies to take.”
Experts emphasize that the ROK government should plan a strategy in the direction of choosing both rather than thinking about the alternative whether it is a China-led RCEP or a Japan- or US-led CPTPP.
Sang-Ryeol Shim, a professor at the Kwangwoon University School of International Trade, said: ‘Ultimately, it is a loss for Korea, which is an export-oriented economic structure, to get out of the Regional Free Trade Agreement.’ ‘. It’s okay to have one more. ”
Sejong = Reporter Cho Hyun-suk and Ha Nam-hyun [email protected]
[ad_2]