
[ad_1]

Photo = Yonhap News
All major quarantine-related indicators such as Korea’s 19th crown inspection rate, incidence rate, and death rate were investigated to be only at the level of the world’s middle ranges. As the number of corona-confirmed cases skyrocketed in recent years, related indicators have deteriorated significantly.
On the 16th, Hankyung.com News Lab analyzed data on the current state of Corona 19 around the world on the global statistical site Waldometer. The most positive). At the beginning of August, it was around 280, but the ranking has increased significantly with the recent increase.
The problem is that the incidence rate is more likely to increase. This is because Korea’s inspection rate (6.7%) is only 130th (the higher the more positive). It is the lowest among developed countries. That means there may be many “hidden confirmed cases.” The incidence rate is expected to rise further, as the government has recently begun to increase the testing rate, such as significantly expanding testing for asymptomatic patients.
The fatality rate (number of deaths compared to the number of confirmed cases) was 1.35%, ranking 130 (the lower the ranking, the more positive). It means that 1.35 out of 100 people will die if diagnosed with Corona 19. It is a low level among all countries, but it is difficult to call it an advanced country for quarantine. Even so, the case fatality rate has declined due to the recent skyrocketing increase in confirmed cases falling below the denominator. The death rate in early August was 2.1%.
Experts noted that in Korea, like Italy and the United Kingdom, the number of deaths from corona19 in the elderly and vulnerable groups can suddenly increase.
Korea’s testing rate is the latest in the OECD, but the death rate is high
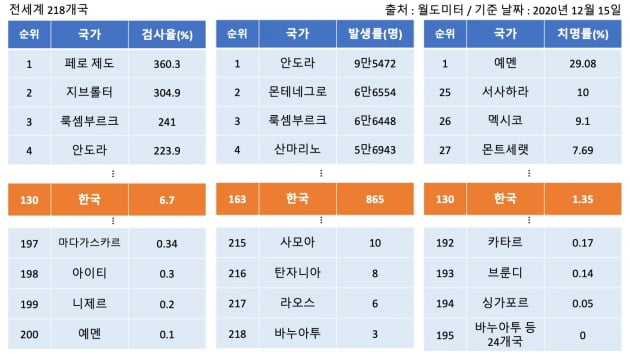
Corona 19 test, outbreak and fatality rates in 218 countries around the world. In Korea, the testing rate was 130, the incidence rate was 163, and the fatality rate was 130. / Graph = Reporter Shin Hyun-bo, Hankyung.com
The weakest part of Korea’s quarantine statistics is the number of inspectors. Korea’s COVID-19 test rate (the number of inspectors per million people) was 6.7%, ranking only 130 out of 218 countries in the world. Only 7 out of 100 have been tested for Corona 19. It is noted that the reason the incidence rate drops significantly is because the testing rate is low.
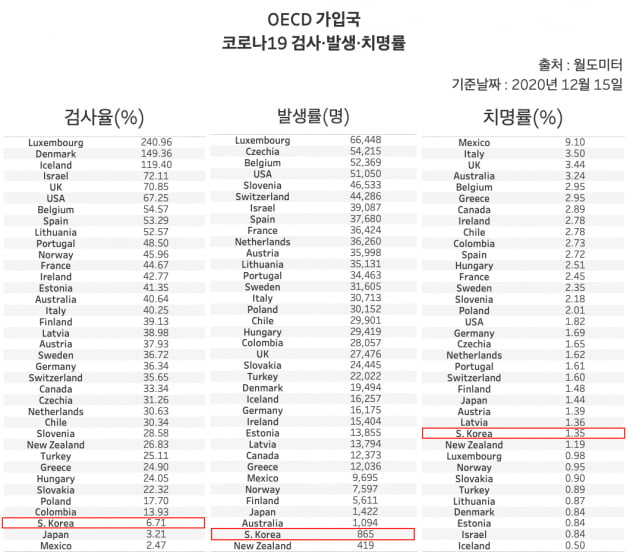
Corona 19 test, outbreak and fatality rate of 37 OECD members. Among them, the test rate in Korea was 35, the incidence rate was 36, and the death rate was 27. / Graph = Reporter Shin Hyun-bo, Hankyung.com
As for the OECD countries, the test rate performance is worse. It ranks 35th out of 37 countries, third behind Mexico and Japan. The incidence rate was 36, the lowest level among the major countries, and the death rate was 27, the lowest level. Among the major countries, the inspection rate is very low, which means that the incidence rate is very low, while the death rate is quite high.
Among the major countries, Luxembourg, Denmark and Iceland are the best quarantined countries. These countries have the highest testing rates, but both incidence and death rates are at the bottom.
Korea, an ultra-aged society, to reduce the death rate
In general, increasing the test rate can increase the incidence rate and consequently the death rate can decrease. Since the case fatality rate is a method of dividing the number of deaths by the number of confirmed cases, the case fatality rate may decrease as the number of confirmed cases increases. However, experts note that there is another cause for concern due to the increasing number of confirmed cases in Korea. It’s that Korea is an “ultra-aged society.”
It’s well known that older people are vulnerable to Corona 19, but the severity of Corona 19 data around the world is mounting more clearly. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 80% of the people who died from COVID-19 in the United States are 65 years of age or older. In Korea, 95% of Corona 19 deaths were found to be more serious than in the United States. It was found that Corona 19 domestic mortality rate and mortality rate are higher with age. As such, it is analyzed that the causal relationship between age and vulnerability to the virus is large.
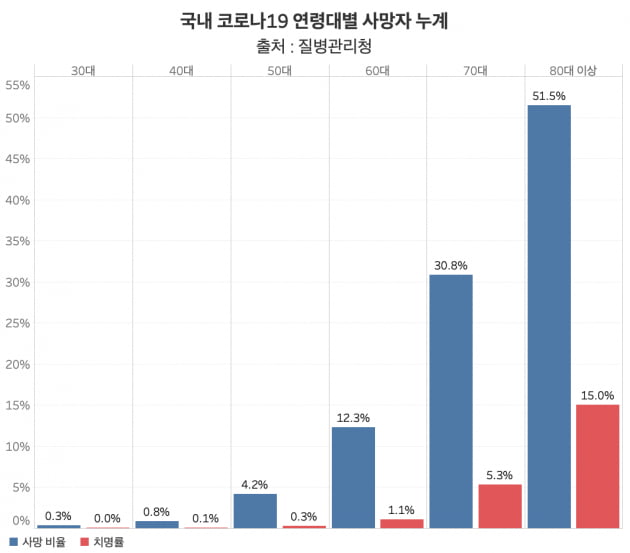
Cumulative number of deaths by association with Corona 19 in Korea. 95% of deaths are older than 60 years. / Graph = Reporter Shin Hyun-bo, Hankyung.com
Kim Woo-joo, professor of infectious medicine at Korea Daeguro Hospital, said: “Countries with a high death rate among the top countries are generally high-aging countries, but Korea is also one of the vulnerable countries due to a extremely aged society. ” “It’s the key,” he explained. Professor Kim said: “Since there is a possibility for young people to meet at the temporary screening clinic, we need to come up with more ways to manage the elderly and vulnerable.”
In a report on the 13th, the CDC recommended a plan of care for the elderly, saying the risk increases with age. Earlier, the Danish embassy in Korea, one of the advanced countries for COVID-19 quarantine, emphasized the importance of caring for the elderly and local administration through a workshop called ‘Coping measures of Covid-19 in a society that gets old ‘in July.
Furthermore, there are opinions that the development of “non-contact” elderly care services should be accelerated in terms of quarantine. Currently, Seoul and some regions are piloting remote health counseling services, but utilization is noted to be poor in terms of accessibility and convenience. In a recent report from the Korean Institute of Health and Social Affairs, Hae-in Hae-in said, “Remote treatment is a useful tool for vulnerable groups with little access to mental health services,” using a smartphone app to telemental (Telemental). It was suggested that the service be improved.
Shin Hyun-bo, Reporter for Hankyung.com [email protected]