
[ad_1]
Check-in: 2020.12.10 17:39
“There are a lot of things to log in and install Active X and keyboard security, and what the heck are you doing!

The hidden camera contest, which complains about ActiveX and the accredited certificate posted on the YouTube comedy channel, recorded 680,000 views, winning the sympathy of numerous people.
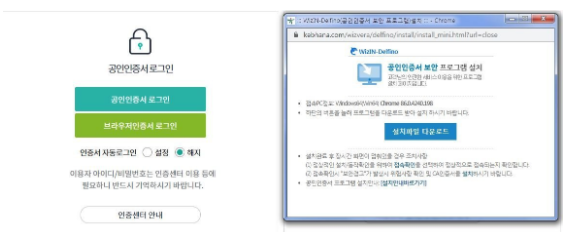
Meanwhile, to be able to use the Internet, mobile banking, or obtain self-authentication on a public institution’s website, it was necessary to use a public certificate based on ActiveX. To download the certificate, it was necessary to download and install various security programs such as firewall and keyboard encryption.
After installation, it was possible to use a 10-digit password that included special characters. If the password was wrong more than 5 times, the certificate had to be re-created, so I had to memorize it in my head all the time. In order to use the certificate stored in the computer on the mobile, the certificate had to be copied and exported, and to use the certificate issued by a bank in another bank, there was also the hassle of registering the certificate again.
The accredited certificate, which was talked about a lot and many masks, was finally abolished. Twenty-one years have passed since its introduction in 1999. This is because as of December 10, the revised bill of the Electronic Signature Law was applied, with the aim of repealing public certificates.
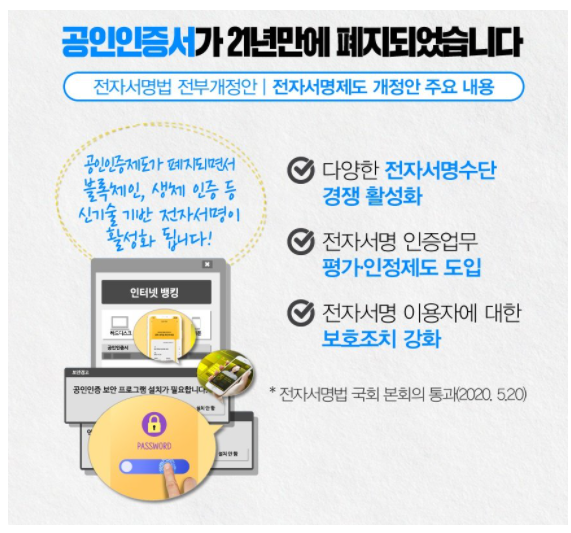
-What will change if the official certificate goes away?Now the name is changed to a joint certificate instead of a public certificate. Joint certificates can be issued through individual financial institutions or private authentication services such as Kakao Pay, PASS, and toss.
-Can I not use the public certificate with the remaining expiration date?
Existing certificates can be used up to the validity period. After the validity period is over, you can renew the joint certificate or obtain a private certificate for your use.-Is there a difference between the certificate received from a financial institution and the certificate received from a private certification institution?The financial certificate received through the bank window, Internet or the mobile banking authentication center menu can be stored in the KFTC cloud and used independently of the computer or mobile device. The certificates can be used by 22 banks and card companies. The validity period is 3 years, which is longer than the current 1 year, and an automatic extension is possible. Instead of the traditional 10-digit password, you can access it through your fingerprint or PIN number. Private certificates can be obtained through each certificate authority application. There are differences in authentication methods and places of use by the certificate authority, so it is better to compare and receive.
-Can I trust a private certificate?
The government says certification authorities assess whether they have basic security measures in place when issuing certificates and whether they provide services through a reliable process. The plan is to ensure security by introducing a strong authentication method for high-risk financial transactions.-Can I use a new accredited certificate for year-end settlement this year?
The government plans to allow the use of private certificates for year-end settlement from the beginning of next year. Five companies, Kakao, KB Kookmin Bank, NHN Payco, PASS and Korea Information Certificate, are said to be candidates. At the end of this month, a pilot operator is selected so that the certificate can be used starting next year.-When and why was the revoked public certificate created?
The accredited certificate was developed in 1999 for the purpose of verifying identity on the Internet. The government has selected six certification agencies, including the Korea Financial Telecommunications and Compensation Institute, the Korea Information Certification Authority, and Koscom, and has granted them exclusive status for certification. The amendment to the Digital Signature Law, which became the legal basis for the revocation of public certificates, removes the superior status of these six organizations and grants the authority to issue certificates even to the private sector.