[ad_1]
Professor of Health Policy at the London School of Economics, Elijah Mosialos, analyzed the latest data on his new executive coronavirus.
Elias Mosialos posted on Facebook in detail: “The spread of the new strain of coronavirus is responsible for the introduction of strict category 4 restrictive rules for millions of people in London and New England, as well as the imposition of travel bans from other countries to the UK.
With the data so far it appears that he is the dominant executive in London and:
- probably more easily transmitted, but data is still being collected.
- It appears that vaccines will continue to work against the new strain.
- Furthermore, it does not create a more serious clinical picture and there is no greater risk of reinfection than this strain.
- The concern is that if it is transmitted more easily, more people can get sick in a shorter period of time, and this will put more pressure on the health system in the coming weeks.
Let’s look at some more details about the situation.
Constraints refer to the attempt to reduce the spread of the variant. Various simulations are currently underway to predict spread, but given the limited data on the virus itself, what is due to human behavior (i.e. public health measures) and what is due to the virus itself. it is difficult to quantify.
Prime Minister Boris Johnson said the variant could be up to 70% more contagious, but that is still being studied. Currently, all studies are in an early stage and there are uncertainties and a list of unanswered questions. Let’s say here again that viruses are constantly changing. What matters is not the changes, but whether they concern us: if the changes detected in the virus ultimately affect the clinical picture, that is, the symptoms and the disease itself.
How did it appear?
The variant is believed to have occurred in a patient in the UK or was imported from a country with less capacity to monitor for coronavirus mutations.
How did it spread to the UK?
The new strain was first identified around September, in November, accounting for about a quarter of cases in London and reached nearly two-thirds of cases in mid-December. Data from Nextstrain, which tracks the genetic sequences of samples around the world, also suggests that the cases in Denmark and Australia come from the UK.
How fast does it spread?
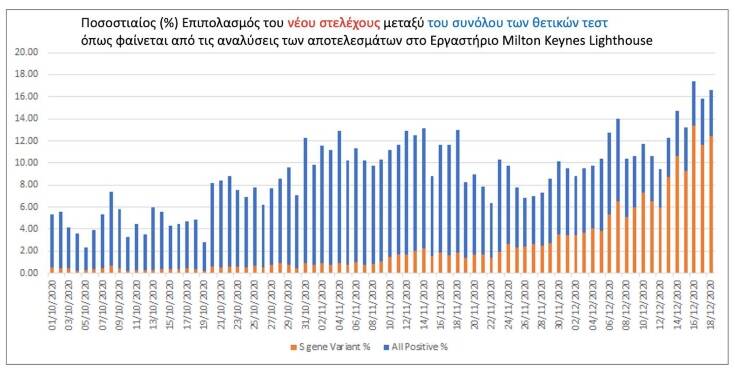
You can see from the attached chart how the new strain has dominated test results at some diagnostic centers, such as the Milton Keynes Lighthouse Laboratory.
Why is the new executive a cause for concern?
Because there are laboratory results that show that some of the mutations it carries are likely to affect the virus’s ability to more easily infect cells. However, there is no absolute certainty and laboratory experiments are required. But restrictive measures are the only way to prevent amid such serious concerns until it is proven whether the new strain is more contagious or more dangerous.
Were there other variants that dominated the virus that was first detected in Wuhan?
Yes.
The D614G mutation appeared in Europe in February and became the dominant form of the virus in the world. The A222V, spread throughout Europe and was associated with the summer holidays of the people in Spain. Another mutation, an H69 / V70 deletion, in which a small part of the pin is removed, has appeared several times before.
What do we know about the new executive?
An initial analysis detects several changes, but if changes in the spike protein make it easier for the virus to enter cells, it is likely to give you an advantage. But this has yet to be proven to be the case.
Does it make the infection more deadly?
There is no evidence that it does, but it is obviously being studied and monitored. However, an increase in transmission alone would be enough to cause problems for hospitals due to increased imports.
Is there a risk of reinfection?
According to the ECDC (Threat Assessment Report 12/20/20), there is no evidence to suggest that it increases the likelihood of reinfection.
Will vaccines work against the new variant?
For now, experts believe there is no cause for concern. Vaccines train the immune system to attack various points on the needle, so if one part has changed, the vaccines should still work.
This would put us in a flu-like situation, where vaccines are regularly modified and continue to protect us. “Experts say that vaccines that have been approved and are being developed are easy to modify.”
New for the new strain of coronavirus
The spread of the new coronavirus strain is responsible for the introduction …
Posted by Elias Mosialos on Monday, December 21, 2020
[ad_2]