The car-sized rover, which landed on the surface of Mars on February 18, has been diligently interested in the planet ever since. One of the questions that has been asked in recent weeks, where is it in the current night sky?
Mars has actually been a popular object in the evening space for several months, and in fact at one point last October it was the third-brightest object in the night sky.
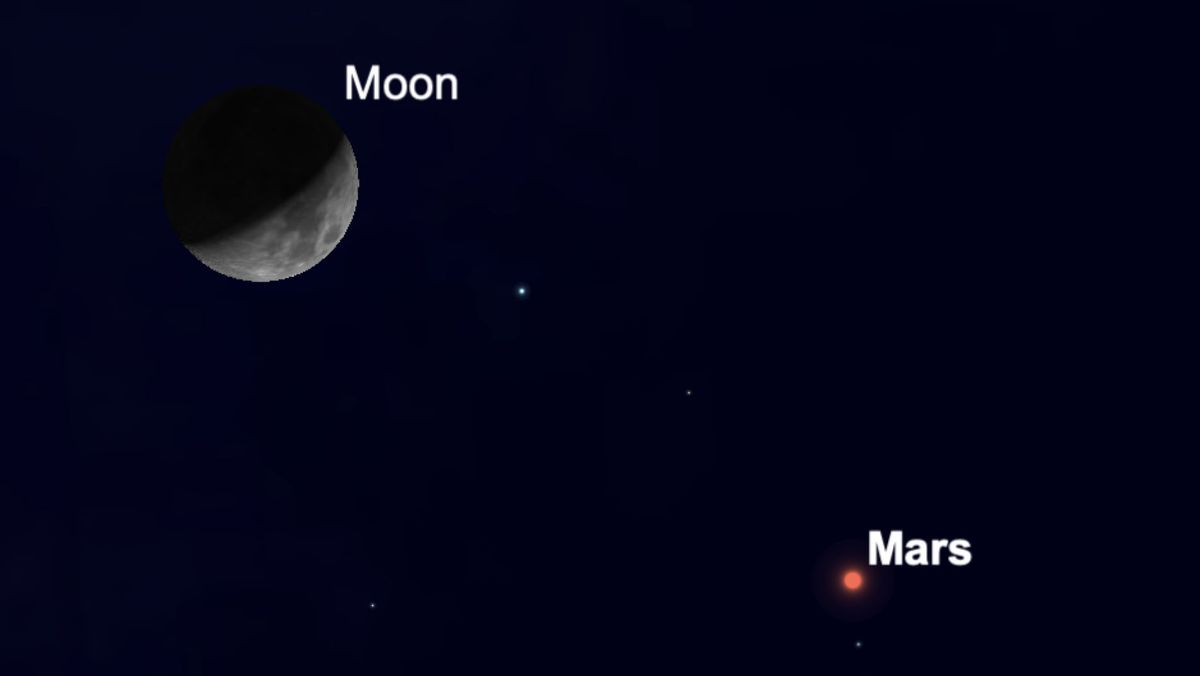
But that has all changed and since then the brightness of Mars has dropped significantly. However, it is still easily visible to the unaided eye and on Friday evening (March 19) you will be able to easily recognize it because of its proximity to the nearest neighbor: the moon in space.
Related: Best Night Sky Events of March 2021 (Stargazing Maps)

On a Friday evening night, look more than halfway across the west-southwest horizon. There you will see a crescent moon, 35% illuminated. And going to its lower right would be a moderately bright yellow-orange “star.” But it’s not a star – it’s Mars, which keeps coming down from Earth and as a result it keeps going. And it can be hard to believe that about 5 months ago it became about 33 times brighter.
On Friday it will be 153.3 million miles (246.6 million kilometers) away and will shine at an intensity of +1.2; In the list of 21 brightest stars, Mars is currently ranked 18th; In early October of 2020, when that bright planet was shining with the brightness competing with Jupiter. In terms of apparent size, the disk of Mars is fairly small; Only a large amateur telescope is likely to show any possible traces on it.
Related: 2021 full lunar calendar

The distance separating the moon from Mars will be about degrees, which, in terms of angular size, is slightly greater than the length of the three stars that make up the belt of hunters, Orion.
Mars 1942 Redux
The orbit of Mars, like Venus, has an echo with the Earth, although it is a little simpler: for the Earth 79 times around the time of going around the Sun, Mars is about 42૨ times around. Thus, Mars travels slightly more than half of its orbit around the Sun each year on Earth. If it travels exactly half, we will pass Mars – that is, there is opposition – every other year, in the same month and place. That being said, protests happen about once every two years and about 50 days.
So now, Mars is repeating its behavior in 1942, years ago. What is always different is the way other planets connect with their revolving arrays. Mars is usually involved in many more connections – i.e. it shares the same spatial longitude and seems to form a closer approach to other object objects in the night sky – than it does to go a long way around our distance. .
Mars is currently located opposite the Taurus stars, the bull. In fact, it rotates about 7 degrees to the left above the star which is remarkably bright: Aldebaron, which marks the bull’s angry eye. And indeed, in late March 1942, Mars had a very similar alliance with Aldebaran.
Just don’t confuse the planet with the stars! Both objects will be the same orange color, but on Friday night Mars will be a dimmer and closer object to the moon.
J Rao Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at the Hayden Planetarium in New York. He writes about astronomy for Natural History Magazine, Farmers Almanac and other publications. Follow us on Twitter @speed.com and Facebook.