New Delhi: A study of data and images sent by ISRO Mars Orbiter Mission (Mom) And NASAMars’ orbit The Martian Atmospheric and Volatile Evolution (Maven) has discovered that “Mars is rapidly losing its atmosphere in outer space.”
In fact, other terrestrial planets in the solar system are also constantly losing their atmosphere in outer space. The rate at which this damage occurs is determined primarily by the size of a planet and the temperature of the atmosphere above it.
As Mars is a small planet in comparison Earth, It is rapidly losing its atmosphere.
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) on Wednesday posted on its website the findings of scientists who studied data and images sent by MOM and Maven about the global dust storm that engulfed the Red Planet in June-July 2018. One such global storm is the dynamic weather event on Mars.
After launching on November 201, ISRO launched Rs. 450 crore MOM was put in the orbit of length. However, according to the space agency’s plan, the MOM will only last six months, even though it is alive and about seven years after its launch, sending images from time to time and has since obtained some key findings about the red planet.
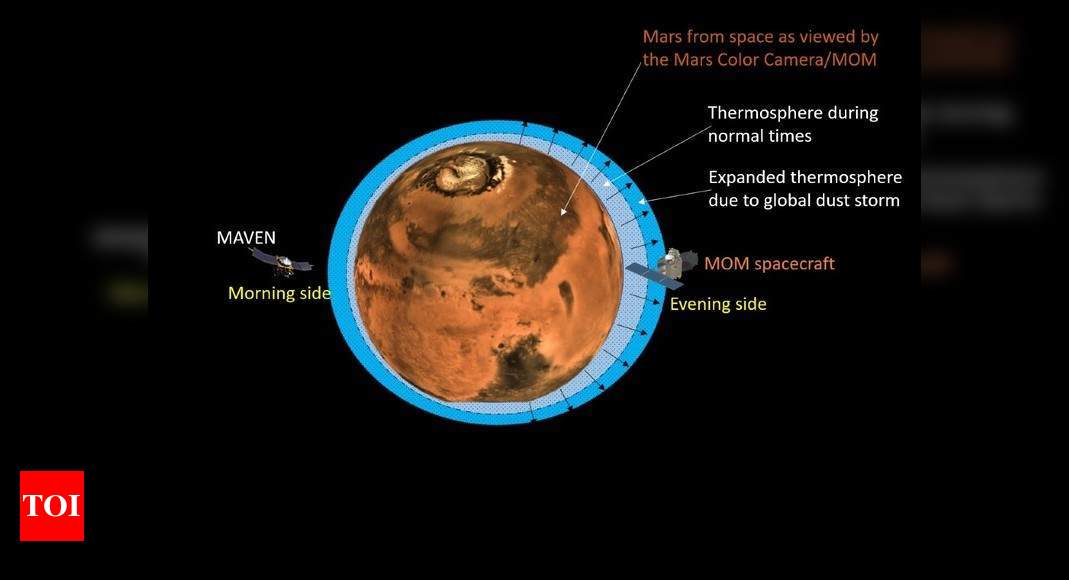
“In the first week of June 2018, the global dust storm, also known as the” planet-shattering dust event “, began to grow on Mars and reached its maturing stage by the first week of July,” the ISRO statement said. Such storms significantly warmed and expanded the Mangalian upper atmosphere.
Due to the heat and expansion of the global dust storm, part of the Martian atmosphere quickly reached an altitude (located at 220 km). Any hot gases above the exoskeleton altitude are more likely to move at higher altitudes and then escape into outer space.
Therefore, from the results of the present study it can be inferred that the result of escaping into the atmosphere of Mars due to the 2018 global dust storm has been achieved. ”
MOM dived to an altitude of 155 km below 155 km and observed the side on Tuesday evening. The Mars Exospheric Neutral Composition Analyzer (MENCA) instrument, a mass spectrometer mounted on an ISRO orbiter, measured the neutral density of Mars. Atmospheric (Which lies between 100 and 200 km).
Analyzing these criteria, scientists at the National Atmospheric Research Laboratory in Gadanki, Andhra Pradesh, found that the atmosphere on Mars is warming and expanding. As dust storms gradually eclipsed Mars over a period of one month, scientists have discovered a significant increase in neutral density in the Martian atmosphere. Such an addition was also confirmed by NASA’s Maven mission, which was simultaneously measuring the Martian atmosphere in the morning, Nissa said.
Both ISRO and NASA spacecraft have seen a significant increase in neutral density in the Matian upper atmosphere (150-22 km) associated with the development of global dust storms in the lower atmosphere.
The study, the scientific results of which have recently been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Planet, highlights the scientific potential of ISRO’s MOM and the benefits of multi-spacecraft measurement in exploring the planet’s atmosphere.
In the video: In ISRO’s MOM study, Mars is believed to be losing its atmosphere
.