
[ad_1]
“Based on the main economic development scenario updated by the Bank of Lithuania economists, the country’s economy is expected to contract by 2% this year, and GDP is expected to grow by 1.9% next year,” he said .
However, the uncertainty about the consequences of the pandemic for the economy remains high, which is why the Bank of Lithuania evaluated alternative scenarios. COVID-19 vaccines, which have already been approved in some Western countries, offer hope that they will soon be available in the European Union and Lithuania.
“If the pandemic situation is managed successfully and stabilizes in the near future, then economic development would be in a favorable scenario. Under this scenario, the fall in GDP this year would be less – 1.4, and next year growth would reach 4.5 percent.
However, the difficult epidemiological situation requires an assessment of the harsh scenario. If the management of the pandemic took longer and it took more time to implement a medical solution, the negative consequences would be the probable deterioration of the financial situation of the companies and the increase of the problems of insolvency. In the worst case scenario, GDP would contract by 2.7 percent this year and another 3.3 percent next, “the central bank said in a statement.

Previously, the Bank of Lithuania predicted that GDP would fall 2% in 2020 and grow 3.1% in 2021. A forecast from the Ministry of Finance on Monday says that GDP should be 1.5% by 2020. more low, and in 2021 it will grow 2.8 percent.
Inflation will not increase
Economists at the Bank of Lithuania forecast that inflation should not rise in the next few years and will reach 1.1 percent both this year and next.
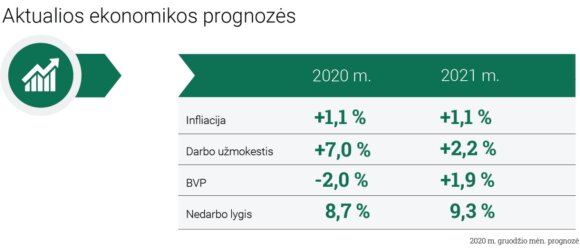
“This year, compared to last year, the growth of the general price level was mainly hampered by cheap fuel, and next year inflation will be limited by slower growth in the prices of services. that the rise in wages will prevent them from rising further and will be much slower than this year.
However, wages are projected to rise twice as fast as prices in 2021, by 2.2 percent. So far, the country’s economy has been relatively resilient to the effects of the pandemic. Although some businesses have been particularly hard hit, the economy has been rescued from a deeper recession thanks to relatively strong industry, increased net exports and government support measures that have helped save jobs.
Limitations and uncertainty in the near future will limit both household consumption and business investment. However, the general financial situation of both the population and the companies allows us to expect positive changes in the future, as the economy returns to normal ”, the report reads.
V. Vasiliauskas said at a press conference that structural changes in inflation can be observed.
“We have tried to break down the factors that make up inflation. As you can see, the factors that reduce inflation are related to those areas of life where there has been the greatest negative impact: tourism, flights, accommodation.
At that time, services like dentistry, medical services, the price change there was really positive. The price increase was modest, apparently due to the additional costs, both safeguards. Also, during the first quarantine, those services were shut down, then opened and the base effect naturally worked, ”he said.

As can be seen in the slide, the prices of dental services increased by 15.1%, those of medical services by 10.7% and those of public catering by 4.7%.
9 percent. deficit
The central bank report also claims that during the crisis, residents and businesses tended to accumulate funds. The amount of household deposits in banks has increased by 11% this year. – up to 17 billion Consequently, corporate funds increased by one third to EUR 8.8 billion. euros.
“During the pandemic, state support and central bank monetary policy measures played an important role, allowing governments to borrow funds on extremely favorable terms. The Eurosystem, of which the Bank of Lithuania is a part, already has invested LTL 700 billion in a pandemic asset purchase program. The total planned volume of the program should reach 1.85 trillion. and will be implemented at least until March 2022.
However, government measures also come at a price, in particular through rising budget deficits and public debt. This year, Lithuania’s budget deficit will amount to almost 9 percent. GDP and will be one of the largest among the EU countries, “the report said.
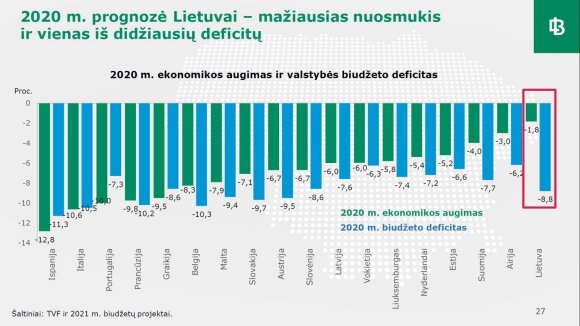
It is estimated that more than 5%. the deficit will be next year and the difference will have to be covered with borrowed funds. As a result, public debt, which has reached a record level this year, will grow to more than 50% next year. GDP.
In addition, there is an increasing risk that public spending will be even higher because the resources needed to manage the pandemic and its consequences are greater than expected. There are also risks to the efficient use of borrowed funds, in particular with regard to the implementation of the DNA Plan for the Future Economy, as it is not clear whether the measures set out in this plan will meet the requirements of the European Commission.
It is strictly prohibited to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, it is necessary to indicate DELFI as the source .
[ad_2]