
[ad_1]
More than 100 different varieties of strawberries are grown worldwide. The scent of wild and cultivated strawberries is legendary worldwide. Scientists now know that esters (including methyltranilate), alcohols, and furanones (including mesifuran) give strawberry a smell. In fact, researchers have even identified a gene called SAAT (Strawberry Acyltransferase Alcohol), which helps strawberries ripen their aroma and flavor.
These berries have a unique combination of various nutrients, phytochemicals, and fiber, and the synergy of these biologically active substances allows strawberries to be called functional foods. Of the phytochemicals in strawberries (containing flavonoids: anthocyanins, flavonols, and flavanols, as well as phenolic acids and elagitanins), anthocyanins and elagitanins are the main and most abundant antioxidant compounds. More than 25 different anthocyanins were found in the strawberries. Pelargonidine is the most abundant. Anthocyanins are responsible for the bright colors of fruits and flowers, they are usually concentrated in the skin of the fruit, but the pulp of berries like strawberries also contains anthocyanins. These substances are very important for the health of the heart. Elagitanins and ellagic acid make up a large proportion of the antioxidants in strawberries. Elagitanins have been linked to important health benefits: fighting bacteria and reducing the risk of cancer.

strawberries
Like other phytochemicals, the most effective way to act for flavonoids is to neutralize free radicals. They are also characterized by antiproliferatives (cell division, especially in cancer cells), vasodilatory effects, and protection against inflammation. Human studies have shown that strawberry consumption increases the antioxidant content of plasma, reduces the oxidation of LDL (low-density lipoprotein, also known as “ bad ” cholesterol) and reduces lipid peroxidation (a process in which free radicals “ remove ” electrons from lipid cells). membranes and therefore damage cells), total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. Oxidative stress, described as an imbalance between the production of free radicals and antioxidant defense mechanisms, is caused by the accumulation of oxidative products, which rapidly increases the risk of cancer, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Eating fresh or frozen strawberries reduced oxidative stress, which is why these berries were even offered as a medicinal food.
Current human study data primarily emphasizes that strawberries protect against inflammation, hypertension, and their antioxidant effects. New emerging studies also demonstrate the beneficial effects of strawberry consumption in the treatment of age-related neurodegenerative disorders, but these claims still require more detailed clinical trials. Therefore, strawberries, as a functional food, allow further research to elucidate and corroborate the preventive and therapeutic effects of these berries on health.
Nutritional value of strawberries. Fresh strawberries are very rich in water, so their total carbohydrate content is really low: 100 grams of the product contains less than 8 grams of carbohydrates, of which the net content is 5-6 grams. Most of the carbohydrates in strawberries are glucose, fructose, and sucrose, but they also contain enough fiber (2 grams of fiber is 2 g of fiber).

strawberries
Strawberries are widely known for their extremely high levels of vitamin C, as well as manganese (8 medium strawberries contain 20% of the recommended daily allowance for manganese), potassium (8 medium strawberries contain 5% of the recommended daily allowance for potassium) and vitamin B9 (250 g of strawberries contain 30% of the recommended daily amount of vitamin B9). Slightly less iron, copper, magnesium and phosphorous, vitamins B6, K and E.
The antioxidant power of strawberries is closely related to the abundance of vitamin C and phenolic compounds. Strawberry antioxidant content was found to be 4 times higher than other fruits, 10 times higher than vegetables, and 40 times higher than cereals. In terms of fruit, strawberries have a higher antioxidant capacity (2 to 11 times) than apples, peaches, pears, grapes, tomatoes, oranges, or kiwis.

strawberries
Studies have shown that the maximum shelf life of strawberries is 2 days; During this time, the berries do not lose much vitamin C and polyphenols.
Storage and storage of strawberries. Recently, researchers carefully examined the shelf life, temperature, humidity, and degree of ripeness of strawberries and found significant differences in nutrient retention. Studies have shown that the maximum shelf life of strawberries is 2 days; During this time, the berries do not lose much vitamin C and polyphenols. There is no way for strawberries to become dangerous to eat or depreciate after 2 days. Just keeping them for a long time loses a lot of nutrients. The optimal storage temperature for strawberries has been found to be relatively low: 2 ° C heat, and public health organizations recommend setting a temperature of 4.4 ° C in the refrigerator as the safest way to store food. Recommendation: If you store a large amount of fruits and vegetables in the refrigerator, including strawberries, it is advisable to set the temperature below the maximum, the range could be 2-3 ° C. When storing food, the composition of nutrients is influenced by four main factors: exposure to air, light, heat and storage time. Strawberries are very fragile, so special care must be taken when handling and storing them. Remove the damaged berries before placing them in the refrigerator. Place unwashed and uncrushed in an airtight container to minimize moisture loss. If strawberries are properly stored in the refrigerator for two days, they will definitely retain all of their nutrients. Do not leave strawberries for too long at room temperature or in direct sunlight, as this will damage them.

strawberries
To freeze strawberries, first wash and dry carefully. You can remove the stems or leave them, depending on what you do with the strawberries when they thaw. Arrange the berries in a layer on a sheet of baking paper and put them in the freezer. Transfer the frozen one to a plastic bag and put it back in the freezer, it is recommended to keep it there for up to a year. Adding a little lemon juice to the berries will preserve their color. Strawberries can be frozen in various ways (chopped, whole, grated), but the highest vitamin C content will remain in the berries without crushing. Results from a study by Polish researchers showed that vacuuming (240 W) was the most effective way to preserve all antioxidants in strawberries (as well as vitamin C), and freeze-dried strawberries had the highest antioxidant capacity. After processing the berries (juice production, puree), bioactive substances (ascorbic acid or vitamin C, polyphenols) are inevitably lost. Canned strawberries or strawberry jam (jam) do not contain anthocyanins or total phenols.
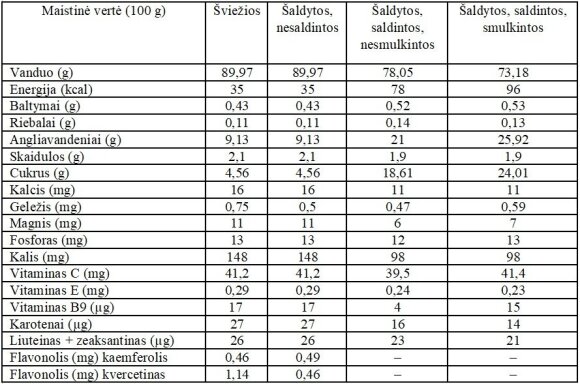
In the table below you can see the differences in nutrients between fresh and prepared and frozen strawberries.
strawberries
So now eat only fresh strawberries, but don’t forget to freeze them for the cold season as well. These are the best ways to preserve the full antioxidant power of strawberries.

strawberries
Sandrija Čapkauskienė – Doctor of Biomedical Sciences, LSU Associate Professor and Nutritionist.
It is strictly prohibited to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, DELFI must be cited as the source.
[ad_2]