
[ad_1]
Although beets are available all year round, their season runs from June to October. There are many species of beets; Only in Europe there are 146 varieties and their hybrids. The different varieties of beets differ from each other in color (yellow, white, pink or deep purple), internal structure, size, leaves and excellent flavor. The early and late winter varieties are the most popular in hobby gardens.

Beet
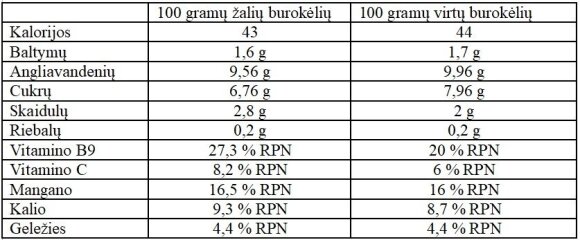
Nutritional value. Green or cooked beets contain about 8-10% carbohydrates. Common sugars, such as glucose and fructose, account for 70% and 80% of the carbohydrates in green and cooked beets, respectively. Beets are also a source of fructans. Fructans are short-chain carbohydrates that can cause unpleasant digestive symptoms in some people. During boiling, the glycemic index of beets increases from 30 to 64-65 units (assigned to the average level of the index). The glycemic index shows how fast blood glucose levels rise after consuming carbohydrates. However, the glycemic load of beets is only 5, which is very low. Consequently, beets should not have a significant effect on blood sugar because the total carbohydrate content per serving is low. Beets are rich in fiber: 100 grams of raw product, about 3 grams of fiber. Dietary fiber is an important part of a healthy diet, it reduces the risk of various diseases.
Beet
Plant compounds. Beets are rich in various biologically active plant compounds. This vegetable is unique for the abundant amount of betaline. There are two main types of betainins, betacyanins and betaxanthins. Betacyanins are purple-red pigments: Betanin is the predominant betacyanin in beets. Betaxanthins (include vulgaxanthin) are yellowish pigments. Betanin and vulgaxanthin are the most studied beet betalains with high antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and detoxifying effects. Betacyanins are the predominant pigments in dark red, red, or purple beets, while betaxanthins, especially vulgaxanthin, predominate in yellow beets.

Beet
Another important compound for human health, which is exceptionally rich in beets, is inorganic nitrates. They are converted to nitric oxide in the body. This refers to the dietary nitrates naturally present in fruits and vegetables. Most research has confirmed the benefits of dietary nitrates for human health: they lower blood pressure, prevent ischemic heart disease, and improve endothelial function. Due to the high content of inorganic nitrates, beets and their juices have a positive effect on heart health and physical capacity. Nitrates are broken down in the human body into nitric oxide, which is an important signaling molecule that performs vasodilation, relaxing and widening blood vessels. Recent studies have shown that nitrates in the diet affect important physiological parameters during exercise: they reduce oxygen consumption during exercise and, therefore, the efficiency of mitochondria, the cellular organs responsible for energy production, improves the muscle contraction and blood circulation, increases functional capacity during exercise. resistance and endurance exercises.
Beets are a great source of many vitamins and minerals necessary for the body: they are rich in folic acid (vitamin B9), manganese, potassium, vitamin C, iron, magnesium and phosphorus.

Beet
Side effects. When eating beets or foods containing beetroot extracts or pigments, in addition to drinking their juices, the urine often turns red or pink. beeturia). The degree of discoloration varies from person to person and depends on the amount of beets consumed. For example, after drinking green beet juice, your urine may be dark red or dark pink. From boiled beets it can be pink or lighter red. Bethanin changes the color of urine in beets (red pigment in beets).
Some people have a hard time breaking down this pigment, causing the urine to turn pink or red. Although this color dissipates spontaneously, red or pink urine after eating beets can sometimes indicate your health problems, so if the color of your urine changes every time you eat beets, talk to your GP. Sometimes this can be a symptom of iron deficiency. The color of urine can also change in people with lower levels of stomach acid. Sufficient stomach acids help the body absorb minerals, nutrients, and vitamins. And low levels of stomach acid can make it difficult to digest and absorb nutrients, so there can be problems processing the betanin from the red beet pigment.

Beet
Beet greens are high in oxalates, which can lead to kidney stone formation. Oxalates can interfere with the absorption of trace elements. The oxalate content in plant leaves is much higher than in roots, but beets are rich in oxalates.

Beet
Consumption. Studies show that heat treatment reduces the concentration of phytonutrients (betalains) in beets. That is why it is recommended to steam the beets for 15 minutes. The same rules apply to their heat treatment as for other vegetables: short cooking times, low temperatures and as little contact as possible with the liquid – low water content. By the way, heat treatment can change the color of beets. Adding an acid (like lemon juice or vinegar) will make the color brighter and an alkaline substance (like soda) can result in a dark purple color for this vegetable. Since salt inhibits the color of beets, add them only at the end of cooking. Also use green beets as an ingredient in salads or soups, marinate in a marinade of fresh lemon juice, extra virgin olive oil and herbs.
Sandrija Čapkauskienė – Doctor of Biomedical Sciences, Associate Professor at LSU and Nutritionist.
It is strictly prohibited to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, it is necessary to indicate DELFI as the source. .
[ad_2]