
[ad_1]
The desire for a lover who has not taken sports more seriously in life sometimes brings more pain than joy.
“Physical activity is necessary for the human body, but you should not overestimate its strength and exercise properly, while protecting your health,” says Marius Šakalinis, orthopedist and traumatologist at Northway Medical Center.
Tennis, basketball, soccer, skiing, waterboarding, running, crossfit, and other active workouts can bring benefits and problems. Therefore, it is recommended to train first with experienced trainers who can advise and correct mistakes.
According to the specialist, even minor injuries, bruises or sprains should result in some limitation of physical activity.
“After an injury, it is especially important to control the bruised and sore spot. If the pain does not go away in a week, you feel instability, visible swelling, you should not wait any longer and consult a specialist. Only in this way can a further increase in the problem be prevented ”, suggests the doctor.
M. Šakalinis, an orthopedist and trauma surgeon at Northway Medical Center, shared his thoughts on knee injuries, causes of pain, and treatment.
– Who usually complains about knee problems?
– A large proportion of patients who report knee problems are young, healthy, athletic, subjected to high stress and injury.
Their wishes are to return the joint to good function and physical activity as soon as possible, so that they can return to their favorite sports, such as tennis, basketball, soccer, skiing and waterboarding, as soon as possible.
– What are the main causes of knee pain?
– There are several types of pain. They can be caused by injuries such as a sudden twist, twist, bump, or unsuccessful descent after jumping through a knee joint. Causes sudden severe pain, limited movement, fairly rapid swelling.
Excessive, prolonged and intense physical exertion may be guilty. For example, a long run for an untrained person, carrying a large weight, in such cases, he feels bathed, chronic pain, bloating.
Knee pain can be caused by chronic diseases, especially in the elderly. Articular cartilage abrasion, osteoarthritis: causes chronic pain, limited movement, joint dysfunction, lameness.
Pain is also caused by inflammation: in the case of rheumatic, infectious diseases, synovitis, certain other diseases and conditions – the joint is inflamed, redness occurs, pain may increase, and the temperature may rise.
– Meniscus tear: how to recognize and what to do?
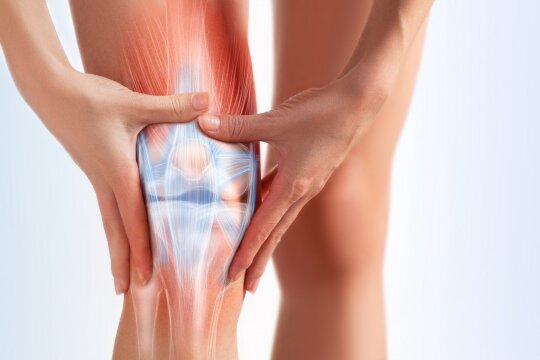
– Diagnosed with greater precision by magnetic resonance imaging (MTR). The meniscus is a cartilage structure tissue located within a joint, which performs cushioning, stabilization and other functions. Vulnerable during trauma or chronic degenerative diseases: osteoarthritis.
Individual treatment is applied: the nature of the meniscus injury (degenerative or traumatic) is assessed, the time is an old trauma or it has just been experienced.
The patient’s activity, age, knee dysfunction (limited movement, pain, swelling, needs or daily activities of the patient, sports, concomitant injuries (condition of cartilage, cruciate ligaments) and treatment are evaluated. One of the treatments most effective is arthroscopic surgery.
It is a minimally invasive surgical method that allows to cure the meniscus problem quite precisely: suturing, repairing a torn meniscus or part of the meniscus. The purpose of the operation is to restore the damaged function of the joint.
In some cases, in the case of chronic degenerative meniscal injuries, when joint function is not significantly affected, non-surgical treatment is applied: physical therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, splints, injections.

© Photo of the organizers
Damaged articular cartilage
– What makes arthroscopic surgery special?
– This is a surgical operation of the knee joint, performed with special equipment, with the help of an arthroscope and specialized instruments and implants.
No massive incisions are used, only minimal incisions of up to 1 cm, non-damaging tissues, faster healing, less postoperative pain, faster rehabilitation and recovery.
– What is the advantage of arthroscopic surgery?
– Arthroscopic knee surgery is performed mainly for the treatment of meniscus injuries, cruciate ligament tear, traumatic and chronic cartilage conditions, in some cases intra-articular fractures, inflammatory diseases.
The advantages are that during the operation there is little trauma to the tissue, there are no large incisions, high precision – precise instruments, special implants and sutures are used. Quick recovery, rehabilitation, and return to function are also important.
– Why after a cruciate ligament injury, if this problem is diagnosed early, is it better to operate after 6-8 weeks?
– Rupture of the cruciate ligaments is one of the most common injuries of the knee joint. When such an injury occurs, there is swelling (blood in the joint), inflammation, dysfunction (inability to fully think, bend the knee joint). After the injury, clinical evaluations, X-rays, MRI examinations are performed.
Usually immobilized (splint, cord, elastic bandage), anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. The acute post-traumatic period lasts for several weeks. After that, the swelling and pain of the joint subside.
Then physiotherapy is needed, exercise exercises – to restore the range of motion of the knee joint, muscle strength, during that time, the necessary examinations are usually performed, an accurate diagnosis is made and treatment is given – surgery : reconstruction of the cruciate ligaments. So the optimal time for surgery is 6 to 8 weeks after injury.
During this time, acute swelling, signs of inflammation, pain, joint movements are restored, and muscles are strengthened. This contributes to better healing, faster rehabilitation, and recovery of function.

© Photo of the organization
Orthopedic traumatologist Marius Šakalinis (photo by Northway)
– Stem cell therapies have become popular all over the world and one of them is LIPOGEMS. Is it true that human adipose tissue can solve complex joint problems?
– Yes, this treatment is gradually gaining popularity, the number of studies showing different results is increasing. It is an experimental method of treatment for degenerative diseases of the articular cartilage: osteoarthritis, chondromalacia.
The patient’s own adipose tissue (fat from the abdominal wall) is used, from which polypotent stem cells are extracted with a special reagent and technique, which are injected into the knee joint.
Stem cells are expected to slow down the degenerative process and affect the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
© Shutterstock
Not only rehabilitation is important, but also motivation
Rūta Burzdžienė, a doctor of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Northway Medical Center, answered questions about rehabilitation after cruciate ligament reconstruction.
– What do you need to know about rehabilitation after successful cruciate ligament reconstruction?
– After the reconstruction of the cruciate ligaments it is necessary to work, and work hard and sincerely. In the postoperative period, the leg launch is partially restricted. Flexion gradually increases, so you will have to walk on crutches and wear a leg splint for 1-2 months.
It is difficult to answer about the duration: you will definitely have to actively work on the road for at least two months, but it happens that even a year after the operation, the movements are not fully restored, because the person was waiting for something, dreaming and such. once was afraid to work actively.
And the more time passes, the more difficult it is to reproduce the movements. Unfolding the plastic knee after the ligaments is quite painful, you really need to work at least a couple of times with physical therapists to focus on how to work hard and actively.
Usually, patients are afraid to actively work with the knee, and it happens that specialists come when they already realize that they are not getting the movements they should. In the course of rehabilitation, various aspects are worked on, depending on the achievements. Working in the direction of restoring range of motion, reducing swelling, activating healing.
After that, a lot of attention is paid to muscle strength, intramuscular coordination, balance techniques, etc., so the tools are very diverse. The base is physiotherapy, but recovery is accelerated with physiotherapy procedures, massages, physiotherapy sessions in the pool, etc.
– Postoperative after arthroscopic meniscus surgery, what do you need to know, is there a risk of premature physical activity and therefore of injury to the leg? When is it recommended to return to active sports?
– After meniscus arthroscopy, things become easier and easier. Usually in the second week after surgery, and sometimes before, it is possible to fully think about the leg and quickly restore range of motion, working with the surrounding musculature.
Of course, until we have improved and restored intramuscular balance, we are not talking about active sports.
It all depends on what was done during the arthroscopy and the surgeon’s recommendations. When returning to active physical activity, you are responsible based on the nature of the operation.
But without a full recovery, without rehabilitation of the knee function and the balance of the surrounding muscles, it is possible to injure yourself even half a year after the operation. If the muscles around the knee are working erratically, some are weak, some are too tight, the distribution of the centers of gravity changes, the friction in the knee joint, and of course the risk of injury increases.
– We know that the rehabilitation of an older person takes longer than that of a younger person. Will an older person who promotes an active lifestyle after meniscus and cruciate ligament surgery enjoy freedom of movement as they did before the trauma?
– Yes, the postoperative healing of older patients, especially those with comorbidities, is slower, poorer. More often it takes longer, more procedures and additional physical therapy sessions are needed.
But I think motivation plays an important role here too: if you lead a fairly sedentary life, you don’t have much motivation to work hard to restore the few missing grades to full breadth. It adapts and you no longer realize that it does not bend completely. The youngest are not without motivation to rehabilitate.
They are often motivated by the desire to safely return to sports activities, so they work with determination and patience until they get the result.

[ad_2]