[ad_1]
At present, in Lithuania, molecular and serological analysis methods are used. They detect different rates of coronavirus infection.
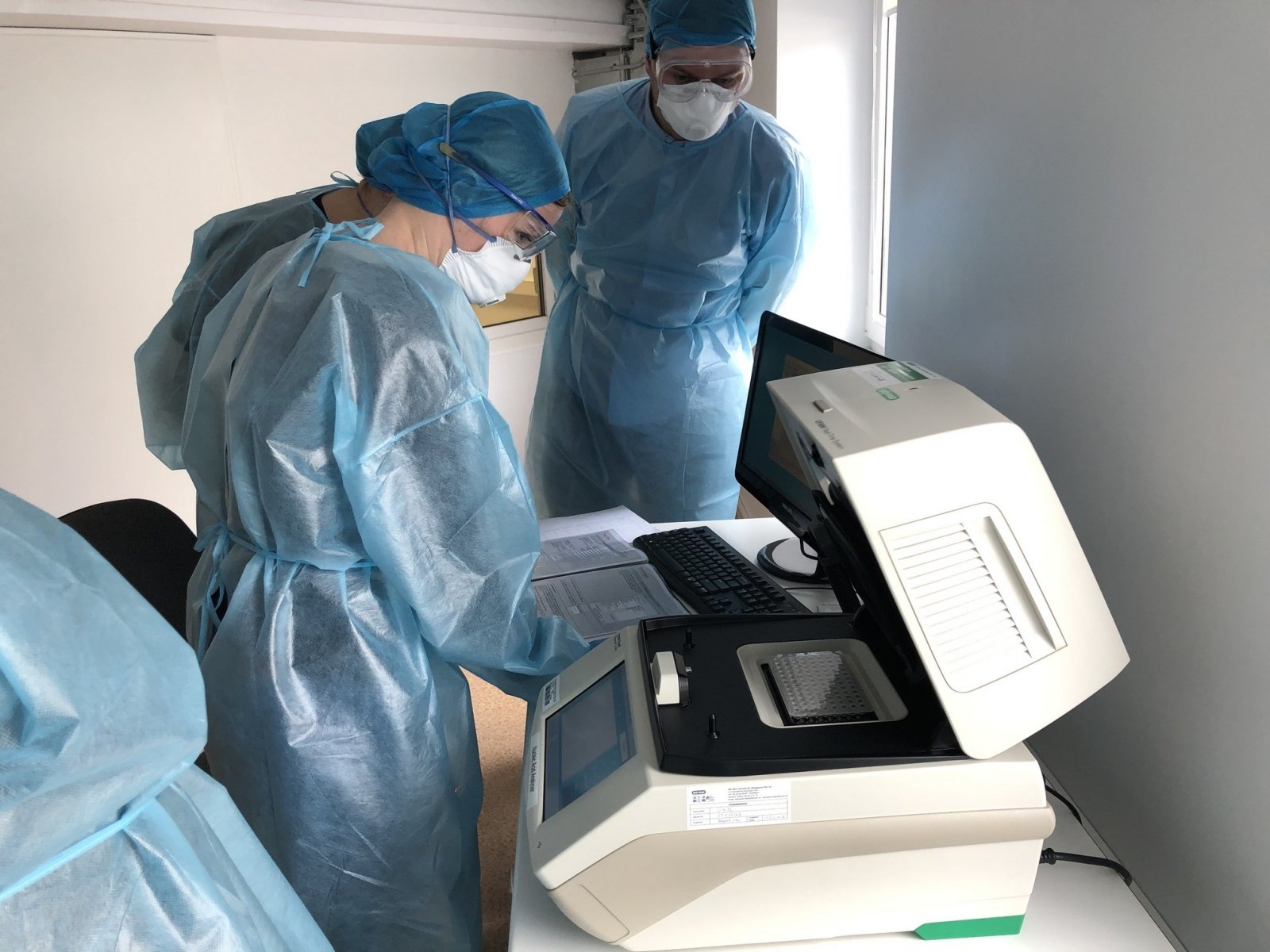
A molecular test that detects viral genetic material (RNA), commonly known as a PCR test, is performed in laboratories and shows if a person is infected with the virus at the time of the test and if they are a potential carrier of the disease. .
To diagnose and cure the disease in a timely manner and prevent it from spreading, PCR tests are first performed on coronavirus-like symptoms when a person has a fever, cough, or shortness of breath. These tests are also performed on people at higher risk, such as those who have returned from countries affected by a pandemic.
These tests are most informative when done in the first week of infection.
The PCR test is performed by taking a sample from the nasopharynx, because the virus enters the human body through a drop of air, through the respiratory tract. In the cells of the respiratory tract, the virus multiplies, allowing the viral RNA to be detected in the sample. The test response is received on average within 24 hours.
When the answer to whether a person is currently infected with the virus and whether there is a potential carrier of the disease must be obtained quickly, a rapid PCR test is performed by taking a sample from the nasopharynx. Response is received within 90 minutes.
This test is performed on urgent patients in inpatient personal health care facilities.
Meanwhile, serological antibody tests aim to discover the products of the patient’s immune response to the virus in the blood: antibodies that have formed in the human body, developing an immune response to coronavirus infection. These tests provide a clearer picture of the epidemiological landscape of the country, manage the spread of this infection, assess how many people are already sick, and what measures are appropriate for further management of the disease.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Rapid serological tests are not recommended for the diagnosis of coronavirus infection., as there are currently insufficient studies on its reliability.
Rapid serologic antibody tests are most informative in the second week of infection, when the immune response to the virus is activated. For the test, blood samples are taken and analyzed, where the formed antibodies circulate. Response is received in 15-20 minutes.
Rapid antigen tests determine if a person has coronavirus. These tests can be performed on people who have coronavirus symptoms or who have been in contact with people with coronavirus, as well as in outbreaks of outbreaks. Rapid identification of infected people helps control outbreaks and regularly monitor risk groups, such as medical, nursing or care personnel.
For people with symptoms of coronavirus, this test can be performed no later than five days after the onset of symptoms, and for people with contact with a confirmed or suspected case of coronavirus, no later than 7 days after exposure. The test is done by taking a sample from the nasopharynx and response is received in 15-20 minutes.
Such a testing strategy, when investigating outbreaks of outbreaks, is also supported by the European Commission (EC), which will donate rapid antigen tests to Lithuania in the coming months.
The EC has entered into an agreement with Abbott and Roche through the Emergency Support Instrument (ESI) under which the EC will purchase and donate rapid antigen tests to the Member States of the European Union (EU).
It is planned to present this evidence to all EU Member States that have expressed the need, including Lithuania, in the first quarter of this year.
The distribution of the tests to the Member States will be based on the expected distribution data, based on information from the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control according to the number of health workers in the countries.
It is strictly forbidden to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, it is necessary to cite DELFI as the source.
[ad_2]