[ad_1]
A million infections every day.
Renata Aleknienė, a family doctor at the Antakalnis Polyclinic, said that more than a million sexually transmitted infections are diagnosed every day in the world.
“The most common symptoms of these infections are lower abdominal pain, unpleasant sensations: pain, burning sensation and altered discharge from the genitalia, ulcerative changes in the mucous membranes of the genitalia. It is very important to note that often there may not be symptoms or are very mild and therefore the risk that these infections will spread more widely, “said the family doctor.
More than 30 different types of bacteria, viruses, or parasites can be sexually transmitted. Currently, the most common are eight sexually transmitted infections, some of which can be easily cured by seeking prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment.

Renata Aleknienė
© Personal album
You can also get infected by kissing
Syphilis and gonorrhea are the second and third most common sexually transmitted infections in Lithuania, which can affect any sexually active person. Gonorrhea, like syphilis, can be passed from an infected person during all kinds of sex: Infected mucous membranes of the genitals can also enter the mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, or anal area.
Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the fact that, even when kissing, there is a risk of becoming infected or infecting another person with sexually transmitted infections.
The doctor mentions the main diseases that can be cured: syphilis, gonorrhea, infections caused by chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
“Unfortunately, not all of the most common sexually transmitted infections can be completely cured: hepatitis B, HIV, herpes simplex virus, and human papilloma virus infections.” Such infections can become chronic and affect long-term health disorders, for example, the oncogenic subtypes of the human papilloma virus can cause cervical oncological changes. Some diseases can be transmitted to a newborn during pregnancy or childbirth, “said R. Aleknienė.

Being with Him, I flew like a free bird, touching the tops of the mountains of love.
A vaccine is mandatory for the control of some infections in Lithuania: hepatitis B, a vaccine against the human papilloma virus.
The main symptoms of sexually transmitted infections are:
– secretions from urine – genital organs (in women they increase), their color varies from yellowish green to translucent;
– pain or burning sensation when urinating;
– white plaque on the penis, vagina, or mouth
– genital rash;
– enlarged lymph nodes in the groin;
– pain in the scrotum, lower abdomen;
– appearance of blood after sexual intercourse.
Sometimes they appear after a week, a month or more, and sometimes there are no symptoms at all.
ULAC doctors recall that chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. It is possible to contract this infection during all types of vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Young and sexually active people are at increased risk of becoming infected.

Chlamydia signs appear 7 to 14 days after infection. They occur in most men, but only one in three women has characteristic complaints.
Clinical signs of chlamydia in women:
– mucous or purulent vaginal discharge;
– pain when urinating;
– blood after sex;
– intercyclical bleeding;
– pain in the lower abdominal area.
Clinical signs of chlamydia in men:
– white or clear urethral discharge;
– burning sensation when urinating;
– scrotum, testicular pain, etc.
When chlamydia infection spreads to the internal genitalia, women develop pelvic inflammatory disease, men develop testicular inflammation and inflammation of the prostate, which can lead to infertility if left untreated. There is also the risk of pregnancy: preterm delivery, miscarriage, and the risk of infecting the newborn during delivery.

Chlamydia
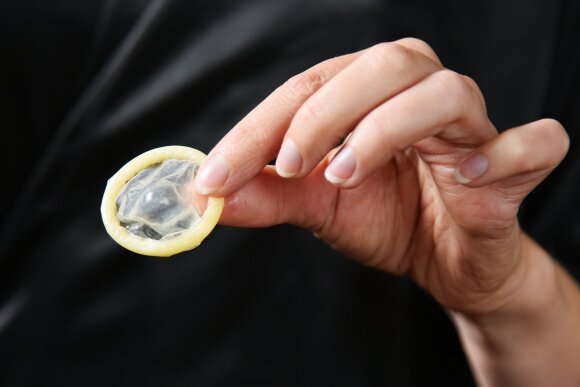
The best prevention is a condom and frequent partner changes.
To protect against chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections, it is recommended to have mutually monogamous long-term sex with an uninfected person, to avoid accidental sexual partners. Consistent and proper use of condoms during all types of sex, especially with casual partners, reduces the risk of infection.
Complications can be avoided and sexual partners protected by regular testing for chlamydia and other infections. Screening is recommended for sexually active youth, after unprotected sex or with characteristic symptoms, when they change sexual partners or if the latter develops signs of the disease, people at risk, and before invasive cervical and other procedures.

Gynecologist
For the test, a sample is taken: discharge from the penis, vagina, or cervix is taken, sometimes from the mouth. Some infections (like syphilis, HIV, etc.) bleed from a vein.
A person infected with a sexually transmitted infection can infect other people from the moment they become infected, even without any signs of the disease. Treatment can only be successful if the sexual partner is treated together, so you must be informed about the disease.
Syphilis symptoms and signs.
For many years, some people infected with syphilis may not have or notice any signs of infection, so they will develop complications of late syphilis. Primary syphilis usually presents with a single ulcer and an enlarged lymph node in the groin area. Secondary syphilis occurs with a rash that begins in one or more areas of the body 3-6 weeks after the primary rash appears on the skin and mucous membranes. Several itchy rashes appear and many lymph nodes are enlarged. Less often, hair falls out or diffuse hair loss occurs, and the eyes are damaged. Damage to the skin and mucous membranes may go away on its own without treatment, but the disease progresses and late syphilis develops, damaging the internal organs. As long as a person does not experience any health problems, which can last for several years, he or she has latent (secret) syphilis.
Syphilis and pregnancy.
Syphilis can be passed to the baby during pregnancy. Depending on how long the pregnant woman is infected, she may have a miscarriage, preterm labor, the birth of a stillborn baby, and the baby may have specific signs of infection or may occur later if treatment is not prescribed.
Unusual discharge from the genital tract, blisters or ulcers, skin rash, and itching are a sign to refrain from sex and to see a doctor immediately.
Gonorrhea complications.
Untreated gonorrhea causes serious and long-lasting complications in both men and women. In women, the most common complication is pelvic inflammatory disease (MDU). The symptoms of MDU may be mild, but they can be very serious, such as acute abdominal pain and fever, chronic abdominal pain, and the development of an internal abscess. MDU damages the fallopian tubes, increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy, and causes infertility. An ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition in which the pregnancy does not develop in the uterus but generally in the fallopian tubes. In men, gonorrhea is complicated by inflammation of the testicular appendix (epididymitis) that, if left untreated, causes infertility.
Gonorrhea and pregnancy.
A pregnant woman infected with gonorrhea can pass the infection to her newborn during delivery. Gonorrhea in a child can cause blindness, a joint infection, or a life-threatening blood infection. The risk of complications is reduced when the infection is diagnosed and treatment is administered.
It is strictly prohibited to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, DELFI must be cited as the source.
[ad_2]