[ad_1]
According to data from the State Health Insurance Fund (VLK), more than 12.5 thousand patients were registered in hospitals last year. Treatment for COVID-19.
Treating hospitalized patients for coronavirus cost the Mandatory Medical Insurance Fund (PSDF) about $ 21.7 million. euros. Additional funds from the state, municipal budgets, and other sources were also used.
According to VLK, treating a patient with COVID-19 in a hospital costs an average of 1.6 thousand. euros. However, there were also patients whose treatment cost exceeded 100,000. euros.
A special system was applied
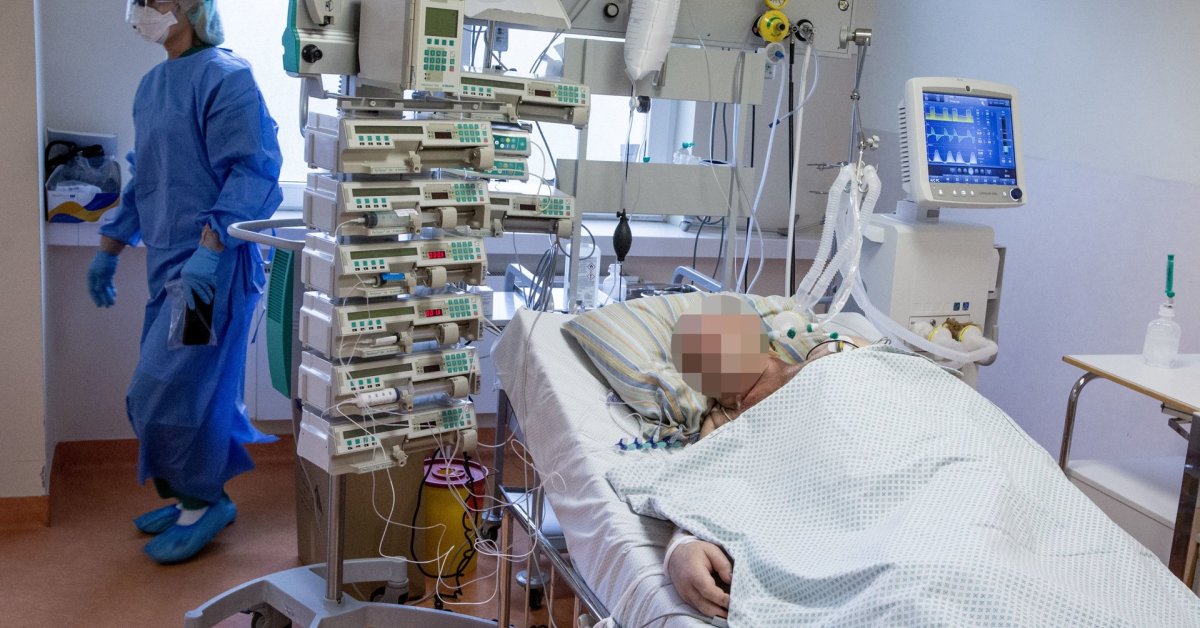
According to VLK data, the most expensive treatment for a COVID-19 patient last year cost 134,000 taxpayers. in case of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (EKMO system).
The cost of treatment for some patients last year was in the tens of thousands.
For example, for the hospital treatment of COVID-19 with long-term artificial lung ventilation that lasted more than 4 days, an average of 8.3 thousand people were paid. EUR (depending on the complexity of the case, the price ranged between 5,000 and 33,000 euros).
If artificial lung ventilation was used for a shorter period, an average of 7,000 people were paid for the treatment. EUR (from 2.5 thousand to 10 thousand euros).

Photo by Vidmantas Balkūnas / Clínica VUL Santara. Fight against coronavirus
Medicines are expensive too
General Director of the Kaunas Clinics of the Lithuanian Health Sciences University Hospital (LSMU) prof. skilled. Dr. Renaldas Jurkevičius 15 minutes He explained that the cost of treatment increases when the patient’s own organs become virtually inactive and their function must be maintained by machines for some time.
“When the patient’s lungs are practically very badly operated, sometimes the artificial pulmonary ventilation system is not enough and the patient has to connect the so-called EKMO system when the human lungs are replaced by a machine,” commented the head of the clinics of Kaunas. the most expensive treatment for COVID-19.
Not only the use of a modern device is expensive, but also additional treatment.
Expensive drugs are used, due to the effect of the virus on the functioning of other systems, sometimes the patient has to connect the artificial kidney, prescribe drugs that regulate the coagulation system or suppress the immune system.
“I am no longer talking about expensive antiviral drugs,” added R. Jurkevičius.
Still, the professor himself said that neither he nor other doctors count how much the treatment costs, leaving this job to the administration and trying to seize every possible opportunity to alleviate the patient’s condition and save his life.

Photo by Erik Ovcharenko / 15min photo / Renaldas Jurkevičius
“Yes, medicine is not cheap these days, especially oncology, cardiology, radiotherapy, expensive immune drugs, cell therapy worth half a million euros, modern and personalized medicine is very expensive. But probably the most precious thing is the life and health of a person, “he said.
Mutations are concerning
When asked if the COVID-19 virus has become at least somewhat predictable over the years, R. Jurkevičius stated that medical institutions have adapted and organize their work differently, but there are still unanswered questions.
He remembered the first case of coronavirus in Lithuania, when on February 28 last year a woman with mild symptoms of COVID-19 was isolated at the Republican Hospital in Šiauliai and was discharged only after receiving the second negative test for COVID-19.
“At first, in the spring, we really didn’t know much about the disease, we were all, as people say, ‘big scary eyes’, and maybe we kept those patients, some of them in mild form, in the hospital, <...> but today these patients are not usually in hospitals, they are treated successfully at home, “he said.
Surprises still arise. The disease is very diverse.
However, it is still difficult to predict how the disease will progress and how the human body will react.
According to R. Jurkevičius, sometimes the human immune system reacts too strongly in response to the coronavirus and its infected cells.
She begins to fight her own cells and tissues to destroy the infected cells.
“It also damages the blood vessels, the kidneys and even the heart. Then we also have respiratory failure, sometimes kidney failure, heart rhythm disorders, inflammation of the heart muscle.
Because many systems are compromised, the spectrum of symptoms is extremely broad, he explained. – Surprises still happen. The disease is very diverse. “
Some patients have to spend several months in the hospital for COVID-19.
Furthermore, according to R. Jurkevičius, the mutated virus and possible reinfections raise new questions. It is not clear if they will be as heavy or perhaps lighter.
Doctors hope that the second time you are infected with the virus, the disease will be less serious, because the body will be able to react, to produce antibodies.
The duration of acquired immunity also remains an unanswered question.
Wants to pay off the “debt” of patients
According to R. Jurkevičius, when it comes to COVID-19 patient flows in the Kaunas region, the situation is not bad: a moderate increase is noted, more commonly known as a “surge”.
However, the burden on doctors, he said, did not decrease, it only changed.
“Doctors feel a certain debt to patients, so to speak, during the last year when they were unable to provide the planned care needed, maybe it was postponed, so only when combat patients, forces regroup immediately and return to treatment is not combat patients ”, – taught the director of the Kaunas clinics.
Doctors feel something of a debt to patients, so to speak, over the last year.
According to the professor, only the emergency department, which worked continuously for 24 hours during the quarantine, received fewer patients and some people were afraid to come.
“Those patients are now more severe, neglected, in later stages of the disease and they really need even more help than a year ago, because those cases are late and the disease is widespread,” said R. Jurkevičius to the consequences of COVID- 19 for the treatment of other diseases.
According to him, it is probably easier for doctors only psychologically: because most medical personnel have been vaccinated, the stress during work has decreased.
“Practically in the Kaunas clinics we have one or two infected doctors in two weeks, who may not have been vaccinated, when we were 20-30 every day in December. It’s really easier for people to work psychologically, we know how to deal with the virus. ” 15 minutes summarized.
In Vilnius, apartments are filling up fast
At that time, in the Vilnius region, where the number of cases of coronavirus infection is higher, the COVID-19 wards of hospitals are filling up rapidly.
Patients are now heavier, careless, in later stages of the disease and certainly need help even more than a year ago.
According to data from March 29, there were only five free beds in the Vilnius City Clinical Hospital branch on Monday, about 80 percent of the beds were occupied in the Santara clinics. places.
Almost full and only branch open in Trakai.
Half of the patients are infected with the British strain of COVID-19 and are also diagnosed with a South African mutation (PAR).
Read more about it – here.

Photo by Vidmantas Balkūnas / Clínica VUL Santara. Fight against coronavirus
More than 800 patients in hospitals
According to data from the Department of Statistics on April 2, 816 patients infected with coronavirus are treated in Lithuanian hospitals, 90 of them in resuscitation.
Oxygen is added to 685 patients and 49 patients receive artificial lung ventilation.
92 people were hospitalized for COVID-19 per day.
A total of 217,865 people have fallen ill with COVID-19 in Lithuania since the start of the pandemic.
[ad_2]