
[ad_1]
Natural vitamin D is not enough
Professor Virginijus Šapoka, director of the Center for Internal Medicine of the Santara Clinics of the Vilnius University Hospital, points out that sunlight is very important for the production of vitamin D in the body. In total, the body produces between 80 and 90 percent of vitamin D through direct exposure to ultraviolet B rays from the sun.
“However, the geographical position of Lithuania determines the lack of sun: in the dark winter months there are no favorable conditions for the production of vitamin D in our country.” And the amount of vitamin D obtained with food is not enough to maintain a sufficient level in the blood ”, says prof. V.Šapoka.
According to the Lithuanian Hydrometeorological Service, the number of hours of sunshine in Lithuania in December is between 8 and 9 times less than in July.

Illustrations by report authors / Sunlight and Vitamin D
The doctor warns that it is in December and January that the cold season begins in Lithuania, when the number of patients with bronchitis, flu or pneumonia begins to increase every week. Morbidity begins to decrease only in the spring.
According to Professor V.Šapoka, a study conducted in Lithuania a couple of years ago showed that a very similar curve is formed when evaluating the number of people whose bodies begin to lack vitamin D. In January, it was found that around 63 per percent of vitamin D is deficient. adult population, and in the spring, up to 75 percent.
COVID-19-19 and vitamin D tteasing: tangible connection
The influence of vitamin D on protection against viral colds around the world has been actively studied for more than a decade. In 2017, research data was released confirming that the use of vitamin D protects against colds and illnesses caused by influenza viruses. For this reason, this year, researchers from different countries have paid special attention to discovering how vitamin D can help fight COVID-19.
One of the first epidemiological studies showed that COVID-19 was directly dependent on vitamin D levels in 20 European countries. Subjects with lower levels of vitamin D in their blood were found to have higher death rates from COVID-19, and subsequent studies confirmed that higher levels of vitamin D reduced the risk of COVID-19 infection. the
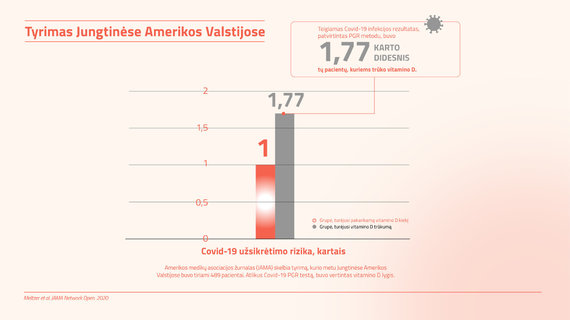
Illustrations by the authors of the report / US Research: COVID-19 and Vitamin D
A study in the United States found that patients lacking vitamin D had a 1.77 times higher incidence of Covid-19 infection than people who were deficient in vitamin D. According to the researchers, the differences were due to the fact that that vitamin D enhances the innate immune response.
The professor explains that, summarizing the results of all current research, it can be said that vitamin D, as a hormone, affects many stages of the interaction of immune cells, even at the genetic level. The evidence linking vitamin D deficiency to COVID-19 severity is indirect but significant: Increased risk factors for vitamin D deficiency match COVID-19 risk factors, such as dark-skinned people , obesity and latitude.
Vitamin D is believed to affect the regulation of inflammatory cytokines (biologically active substances released by cells that help cells develop immune responses), with a significantly increased risk of pneumonia and viral infections of the upper respiratory tract.
Hospitalized COVID-19 patients low in vitamin D have been shown to have more severe morbidity and higher mortality than those with normal vitamin D. Additionally, low vitamin D levels have been shown to be associated with increased thrombotic events due to increased blood clotting, which is often seen in patients with the disease.
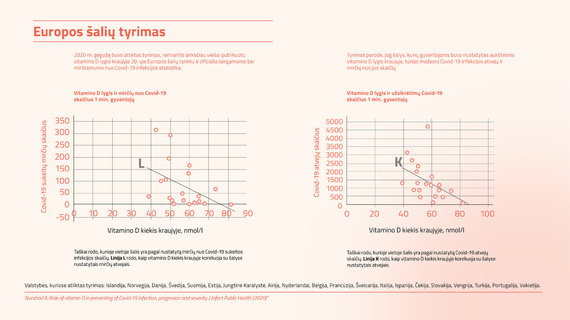
Illustrations by the authors of the report / Research in Europe: Covid-19 and vitamin D
Prof. V.Šapoka points out that residents of northern countries, including Lithuania, do not have the opportunity to naturally maintain sufficient reserves of vitamin D throughout the year. When sunlight decreases, the stocks accumulated in the body during the hot season are depleted in about a month. The professor adds that getting enough vitamin D from food is practically impossible.
“The amount of vitamin D in food is very low. To get enough, for example, a person should drink 3 to 6 glasses of milk or eat 4 to 6 cooked egg yolks a day, and to restore the deficiency of vitamin D, the amount of that food should be doubled, “says the doctor, who advises residents to look for other possible options. sources of vitamin D.
[ad_2]