
Astronomers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have achieved the status of a supernova, a fast, fading celebrity of star extinction. Hubble snapshots have been collected in a movie about the explosion of the Titanic stars that disappeared into oblivion in a spiral galaxy NGC 2525, 70 million light-years away. S.N. It beats the brightest stars in the galaxy before it is initially visible. The time-lapse video includes observations taken between February 2018 and February 2019. Credit: NASA, ESA, and A Recess (STSCI / JHU) and SH0ES team; Acceptance: m. Zamani (ESA / Hubble)
When a star emits as much energy as our sun in a few billion years, you know it won’t be visible for long.
Like the interval paparazzi, NASANo. Hubble Space Telescope Supernova, the star’s fast-paced, fading celebrity status. Hubble snapshots have been collected in a movie about the explosion of the Titanic stars that disappeared into oblivion in a spiral galaxy NGC 2525, 70 million light-years away.
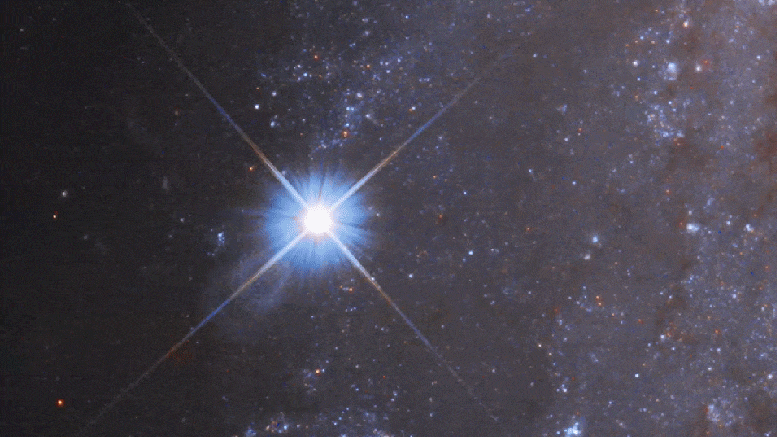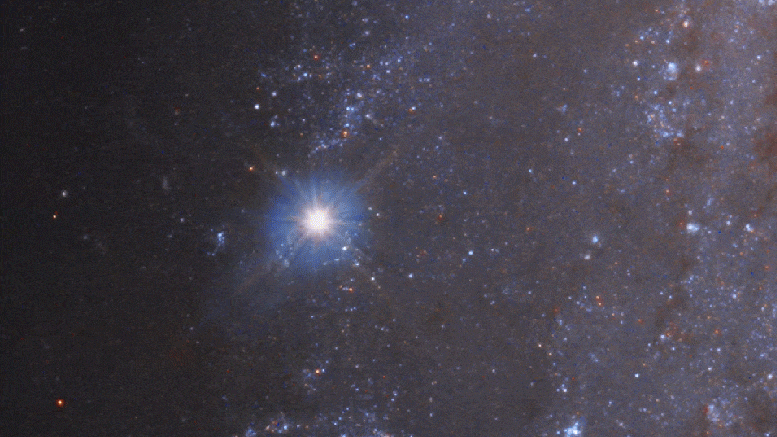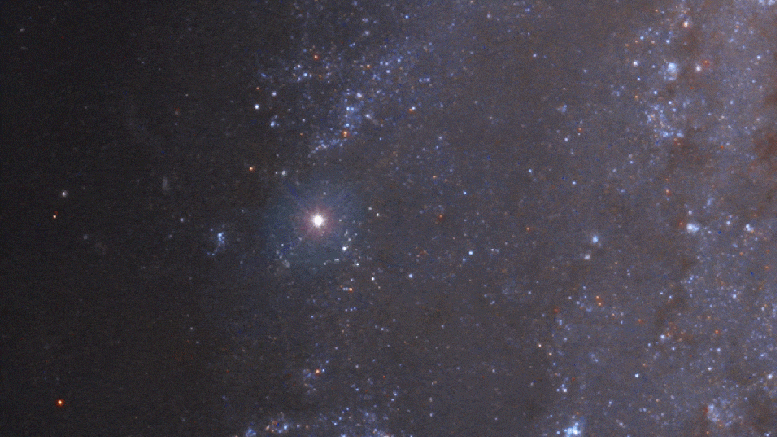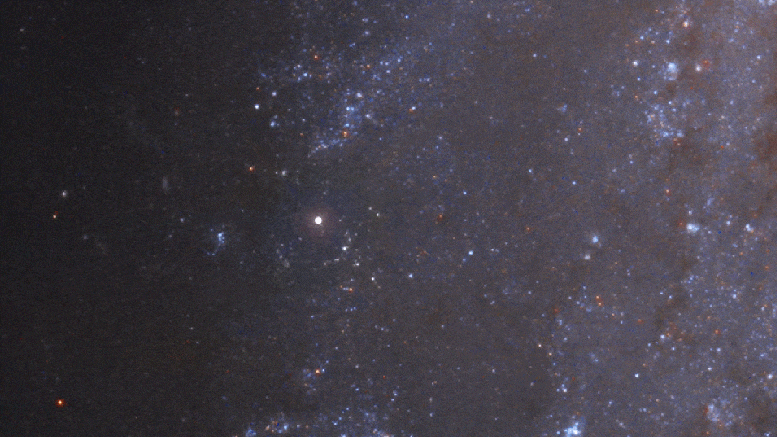
This video zooms in on a blocked spiral galaxy NGC 2525 located 70 million light-years away in the southern constellation Pappi. About half the diameter Milk GangaIt was discovered by British astronomer William Herschel in 1791 as a “spiral nebula”. Image sharpness increases as you zoom into Hubble View. As we get closer to the outer spiral arm, a Hubble time-lapse video is inserted showing the fading light of the Supernova 2018 GV. Hubble did not note the initial explosion in January 2018, but took continuous photos from almost a year from 2018 to 2019, assembled in a series of time intervals. At its peak, the exploding star was as bright as 5 billion suns. Credit: NASA, ESA, J. Deepsquale (STSCI), m. Cornmesser and m. Zamani (ESA / Hubble), a. Reiz (STSCI / JHU) and SHSES team, and Digitized Sky Survey
After the supernova was first discovered by amateur astronomer Koichi Itagaki a few weeks ago in mid-January, Hubble began observing the SN 2018 GV in February 2018. Hubble astronomers were using supernovae as part of a program to accurately measure the rate of expansion of the universe – a key value in understanding the physical evolution of the universe. Supernovae serve as a landmark for measuring the distance of galaxies, which is the basic value required to measure the expansion of space.
In the course of time, about a year later, the supernova first appears as a shining star located on the outer edge of the galaxy. It beats the brightest stars in the galaxy before it is initially visible.

Astronomers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have achieved the status of a supernova, the fast-disappearing celebrity of the star’s extinction. The supernova, called the SN 2018 GV, appears in the lower left of the frame as a shining star on the outer edge of a spiral galaxy NGC 2525, a million million light-years away. Credits: NASA, ESA, and a. Ries (STSCI / JHU) and SHSES team; Acceptance: m. Zamani (ESA / Hubble)
“No Earth fireworks display can compete with this supernova, captured in its evolving glory by the Hubble Space Telescope,” said Adam Tevez, a Nobel laureate from the Space Telescope Science Institute (STSCI) in Baltimore and Johns Hopkins University. Search team and supernova h0 For the Equation State (SH0ES) team to measure the rate of expansion of the universe.
The type of supernova seen in this order is derived from a burning star – a White dwarf Located in the nearest binary system – it is increasing the content of its fellow star. When a white dwarf reaches a complex mass, its main atom is heated enough to ignite a compound, turning it into a giant atom bomb. This thermonuclear fugitive process destabilizes the dwarf. Scientology is short-lived as firefighters are declining.
These types of supernovae are at all luminosity, so they are known as “standard candles”, which act as cosmic tape measures. By knowing the actual brightness of a supernova and observing its luminosity in the sky, astronomers can calculate the distances of their host galaxies. This allows astronomers to measure the rate of expansion of the universe. Over the past 30 years, Hubei has made dramatic improvements in improving the accuracy of the universe’s expansion rate.