[ad_1]
A Bulgarian coronavirus vaccine is being developed at the Stefan Angelov Institute for Microbiology of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences.
All about:
Coronavirus epidemic (COVID-19) 4771
This is a completely new idea, very interesting and hopeful, said Dr. Penka Petrova, director of the Institute of Microbiology of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, in an interview with BTA.
The development of the Bulgarian coronavirus vaccine is partially funded by the Pasteur Institute in Paris..
However, it is too early to talk about the application of clinical trials in mice and humans. At this stage it is not possible to predict when we will have a Bulgarian coronavirus vaccine because the development of a vaccine is a very long process and has to go through all stages, Professor Petrova explained.
The vaccine development project is a two-year project and its leader is Assoc.
Funding comes from a European program and is part of a larger project., implemented by four BAS institutes in the field of biomedicine and quality of life.
BAS scientists are joining forces in this larger project, which will also research antiviral substances, design a drug, search for new approaches to diagnosing viral infections, and develop vaccines.
The BAS Institute of Microbiology cooperates with other BAS institutes to limit the spread of the coronavirus, Prof. Penka Petrova announced.
With the BAS Organic Chemistry Institute, our institute works on the synthesis of antiviral substances.. A scientific team from the Institute of Organic Chemistry of the Center for Phytochemistry has synthesized around 70 antiviral ingredients, analogs of chloroquine and other substances. Chemists are synthesizing the substances and their antiviral activity is being tested at the Institute of Microbiology, the director explained.
Our other serious and good cooperation is with the BAS Polymer Institute, which develops new materials for the creation of protective masks with electrofiber polymers for surface treatment. These are new materials: nanomaterials that can be incorporated into protective masks. At the Institute of Microbiology, it has already been verified that these new materials leak antiviral particles and we have shown that they are very reliable for use in protective masks, said the associate professor of the Petrova Association.
Scientists from the Institute of Molecular Biology and the Institute of Microbiology of BAS help with research related to coronavirus in the laboratory of UMBALSM “Pirogov”. Scientists from the Institute of Experimental Pathology, Anthropology and Morphology of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences have also been developed in this field. Scientists at this institute work in the fields of “Virology” and “Immunology”, explained Associate Professor Penka Petrova.
Two vaccines against the US coronavirus have already been developed. USA And now they are in clinical trials.
One vaccine is from the modern American company, and there is a second vaccine from an American company. These two vaccines from EE. USA They are in the clinical testing phase: they are already being tested in volunteers. This gives hope that in a few months the effects on humans of these vaccines will be seen. The Modernna vaccine will be ready by July and will know its effects on humans, whether it is effective against the coronavirus. But then there will be evidence of cytotoxicity from the vaccine.
“These vaccines are now in the stage of vaccine antiviral action and the ability to create immunity, but there are still stages to investigate. Therefore, it is impossible to talk about a vaccine that will be produced and administered on a large scale before drop”. , said the director of the BAS Institute of Microbiology.
The coronavirus is very small in size, it is not the deadliest coronavirus, but it spreads more easily.
It is difficult to examine directly and can only be seen with an electron microscope. The methods for their investigation are indirect: in cell cultures, explained associate professor Penka Petrova. He reported that the Institute of Microbiology is working with coronavirus analogs, strain 229 E, which is less pathogenic and isolated from people with the common cold. It was supplied by our national bank, but has now been ordered by the American Bank for Cell Culture, reports BAS’s director of microbiologists.
Genetic methods have shown that the coronavirus is a natural virus and consists of the genomes of a bat virus that has also passed through the animal pangolin. It is a typical animal-borne pathogen, and scientists have certainly shown that it is not synthetically synthesized but also attacks humans, said Associate Professor at the Petrova Association. He explained that this is typical of coronaviruses and that the “Middle East Respiratory Syndrome”, the MERS virus, is transmitted through camels to humans. Very often, first-time animals do not contract the disease but serve as a reservoir for viral particles.
The current new coronavirus is not the deadliest coronavirus, the deadliest were MERS and TORS, but COVID-19 is the most invasive coronavirus: it is more easily transmitted and spreads worldwideProfessor Petrova explained. According to her, the new coronavirus has spread as a global pandemic in just a few months due to globalization and travel by people on all continents.
“This new virus began to spread initially among those sectors of society that have a high standard.. These are people around the world who travel a lot, communicate a lot and do not pay attention to anti-epidemic measures, “said associate professor Penka Petrova. She noted that it may have been unexpected for people of high standard of living traveling to different destinations , that infecting the new coronavirus is very easy, which is why it is more frequent in the main cities of the world, such as New York, Milan, Lombardy and Madrid.
“By drawing a parallel between the east and west coasts of the United States, you can see that the New York pandemic is scary and the West Coast coronavirus is less common. There, people are more separated from each other, as a form of residence, “said Professor Petrova.
The coronavirus is not resistant to sunlight, but German scientists have shown that the virus mutates and does not know how it will respond in hot climates.
Due to the looming warm weather, we expect the coronavirus pandemic to decrease, especially due to sunlight, as sunlight destroys the virus and spreads on hard surfaces and on sidewalks. In cities, due to sunlight, the spread of the coronavirus should be reduced due to the opinion of the director of the Institute of Microbiology of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences.
Coronavirus is not resistant to sunlight, until now coronavirus infections have always been considered winter infections.and – like seasonal flu or seasonal infection. However, now we find a new pathogen that has a new genome. German scientists are already known to have discovered that the coronavirus genome mutates with approximately three nucleotides / bases / pairs per month. The virus continues to mutate and alter its genome, and we cannot currently anticipate its adaptive mechanisms in warmer climates.
Rather, we hope that the coronavirus will limit its spread, but the main way we expect it to be limited is by building “public immunity” against the virus. For our country, however, this is not applicable now, since we have a very small number of patients, but in the future, when a vaccine is invented and the population begins to vaccinate, we will already have “group immunity” of people in the country that will. stop its distribution, said Professor Penka Petrova.
He noted that, unfortunately, in countries with hot climates, the coronavirus continued to spread. In Australia, it is summer and it passes to another season, but there are still a large number of people infected and infected with the coronavirus in the country. We hope that this new virus will be stopped by the hot climate, but we cannot be sure, because for the first time humanity is facing an infection with this type of coronavirus, with such a pandemic size, said the associate professor of the Petrova Association.
According to her, “it is possible, for example, in the autumn, that there will be new waves of contamination, since it is not possible to say from now on whether the world will be able to cope with this pandemic.” Compared to other pandemics, for example, TORS / and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), which infect far fewer people, despite the fact that they were more pathogenic and had a higher mortality rate. greater due to the severity of these diseases, they affected fewer people. The new coronavirus can be said to be “gentler on the host and this allows it to spread even further,” explained associate professor Petrova.
Another difference from previous coronavirus infections is that the new virus has a much longer incubation period, and infected people continue to carry it longer in their bodies., compared to other infections. “This will lead to new waves and the world is not ready for the new coronavirus globally. Unfortunately, the healing and cleanup period for viral particles is long.”
The coronavirus is used for a long time, more than three weeks in the blood of migrants., and they have to go through a long quarantine after being sick. This is a global pandemic, “Assoc. Prof. Penka Petrova.
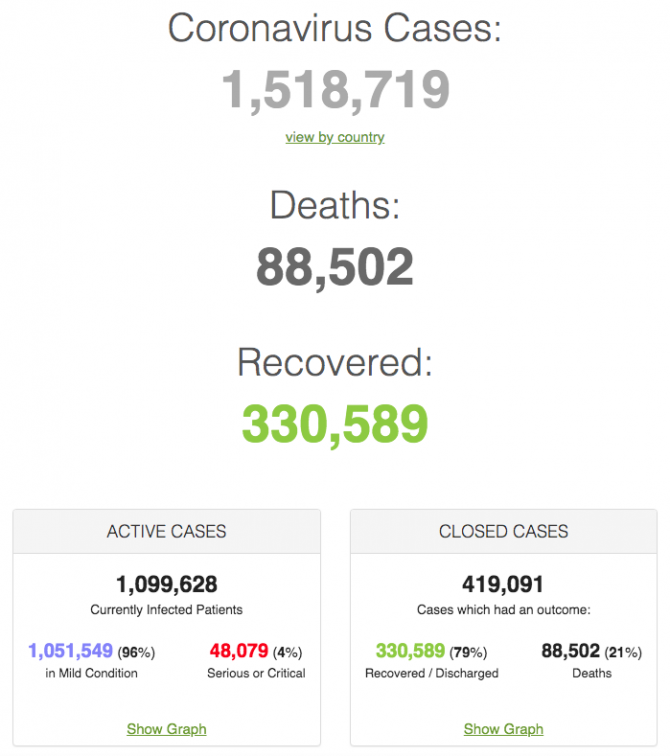
Novini.bg gives you the opportunity to track real-time data on the lethal coronavirus:
More about the coronavirus

[ad_2]