[ad_1]
 The Radeon RX 5600 XT should become AMD’s ideal 1080p gaming card. Ultimately, this goal was accomplished, but the path was more rocky than it should have been. The Radeon RX 5600 XT was featured with a 1,500 MHz (12 Gbps) memory clock and these must remain AMD’s specs.
The Radeon RX 5600 XT should become AMD’s ideal 1080p gaming card. Ultimately, this goal was accomplished, but the path was more rocky than it should have been. The Radeon RX 5600 XT was featured with a 1,500 MHz (12 Gbps) memory clock and these must remain AMD’s specs.
But from the beginning it turned out that not only will individual graphics card manufacturers accelerate their memory to 1,750 MHz (14 Gbps), but this will apply to almost all models. Three other models we tested have already been equipped with a new BIOS. There were a few exceptions, and probably to keep the series’ base price low, some models stuck in slower memory, but it seemed practically possible that almost all manufacturers and all models accelerated memory.
There were a few prerequisites for this: firstly, the storage had to be specified accordingly in advance, and secondly, the cooling system had to be designed accordingly. The models seemed to do both. Memory bandwidth increases from 288 to 336 GB / s and gives the card a 5-10% performance boost.
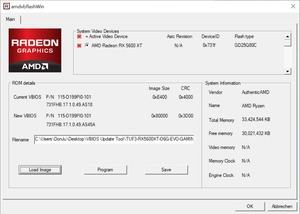
However, according to AMD, it should go like this: The Radeon RX 5600 XT is a graphics card with Navi 10 GPU and 12 Gbps memory and is still preserved to this day. However, external communication has changed somewhat in the meantime. Since 90% of manufacturers now equip their models with the fastest memory, either directly or by updating the BIOS, AMD announces this accordingly. All models are featured on a product page, which can now be accelerated by updating the BIOS.
It seems that the AMD text happens in a mysterious way. A simple BIOS update is sufficient, but we are talking about a higher power consumption or a total graphics power of 120 to 135 W and if the memory could previously work with a higher clock, why AMD does not have this from the beginning? provided?

A soft aftertaste remains. The question still remains as to why AMD did not directly provide the Radeon RX 5600 XT with the fastest memory, although it is apparently possible to subsequently speed up a large portion of the models with a BIOS update.
Instead, buyers of the card first have to see which BIOS is already installed. If the old BIOS is still on the card, the BIOS update process must be performed. Although this is largely risk-free, problems can occasionally arise and, in the worst case, the card must be returned to the manufacturer. This whole process could have been avoided for all buyers of a Radeon RX 5600 XT if they hadn’t played the game in the subsequent BIOS update and equipped the card with the memory set at 14 Gbps, as they obviously had already done.