[ad_1]
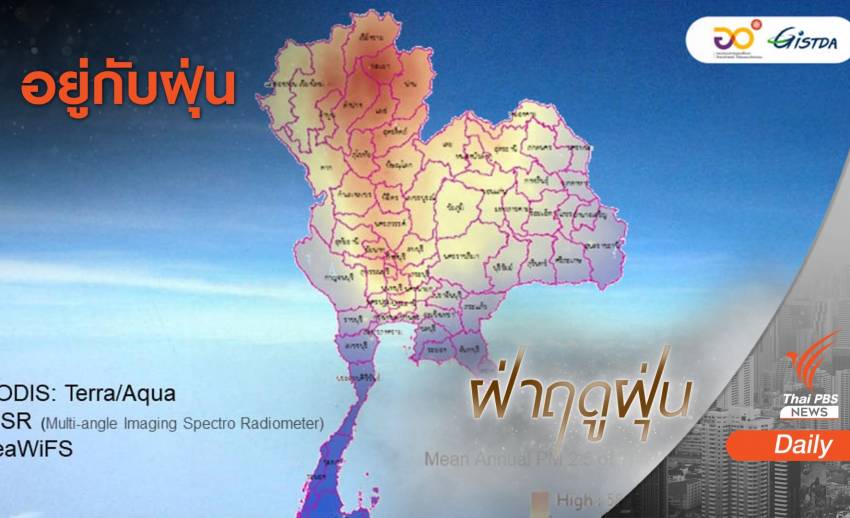
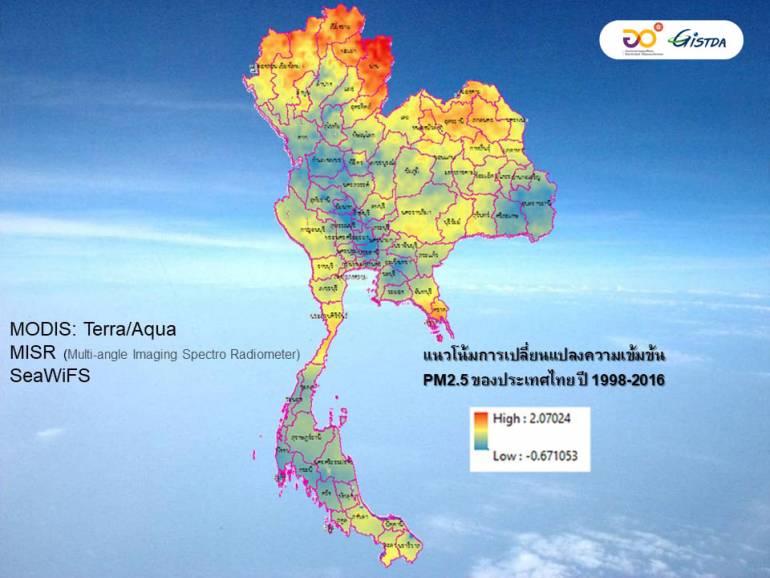
“Jizda” reveals satellite images from 1998-2016, found that Thailand has faced dust for almost 20 years, especially in northern Nan province, Phayao, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai and Mae Hong Son, which are at risk of dust PM2.5. Recently, using a satellite to collect dust 2 times a day
PM2.5 and smog problems in the north It is a widespread spatial problem that has occurred in large cities. To rural and border areas that have serious long-term effects on human health. Including the negative impact on the economy Society and people’s quality of life are enormous.
Today (November 26, 2020), the Facebook page of the Geoinformatics and Space Technology Development Agency (GISTDA) reported that Hoy, the earth observation satellite equipped with a remote sensing sensor. It is capable of providing data on the amount of particles, both PM 10 and PM2.5. The advantage of using satellite data is that the amount of dust in the atmosphere can be measured and reported anywhere in the country. And neighboring countries Including receiving information that is of the same standard Makes it easy to analyze and process.
Using satellite and geospatial data to deal with air pollution. It will greatly reduce the limitations of the use of ground instruments. Continuous implementation of already measured spatial data, such as satellite data from various sources. Both at home and abroad It will help to understand and see a clearer picture in planning to solve PM2.5 problems at the strategic level. Policy-level planning, direction and monitoring Including transboundary pollution monitoring analysis
Read more news the first day! Black smoke detection, 8 cars were immediately banned.
The northern region has faced PM2.5 for 20 years.
GISTDA collects data from satellites. And it was found that Thailand has been exposed to small particles and PM2.5 for a long time, some satellite data indicate the trend of changes in PM2.5 concentrations in Thailand from 1998 to 2016 with a relatively large concentration of concentrations in the North Region.
Especially Nan, Phayao, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, and Mae Hong Son, who have been at risk of excess PM2.5 for nearly 20 years.
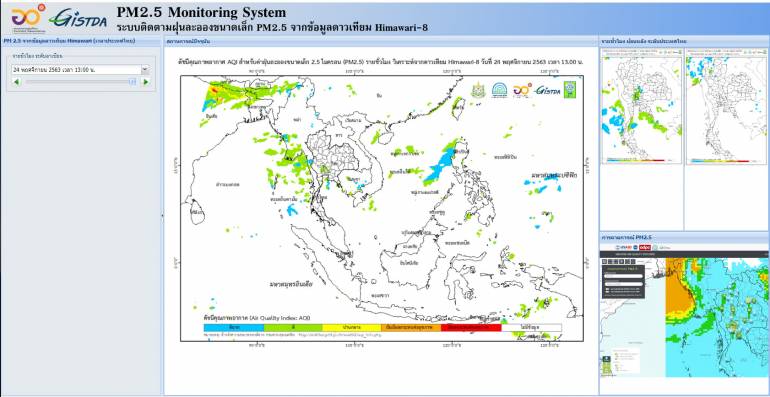
Such information Considered statistical data collected from Thailand Measuring instruments were not introduced a few years ago, just a small dust meter. GISTDA now uses MODIS satellites to monitor the PM2.5 situation twice a day, in the morning and in the afternoon.
GISTDA has also been optimized for situation monitoring using another Japanese satellite, Himawari (Himawari), which delivers fast and accurate data every hour. This will be of great benefit to the key departments involved and can be applied to accurately plan, monitor, investigate and solve problems.
PM2.5 dust is considered a national agenda that many interested agencies have to accelerate to solve the problem. However, editing can take time. But as citizens, we must work together to reduce dust-generating activities. And to regularly monitor air quality To assess the risk of PM 2.5, dust can easily enter the body through the respiratory system.
Most of the reasons are industrial in origin. Industrial plant Various types of construction sites, sea, fuel combustion. Engine combustion Open burns, such as forest areas, agricultural areas, and debris, most of which are incomplete and incomplete combustion. Until it forms a mist or several particles
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dqIhP902RN8
Read related news
“Chiang Mai” adjusted PM 2.5 plan to remove fuel zones
The “toxic dust” broke the record for 4 years with a high value of 366 mcg per cubic meter.
[ad_2]