[ad_1]
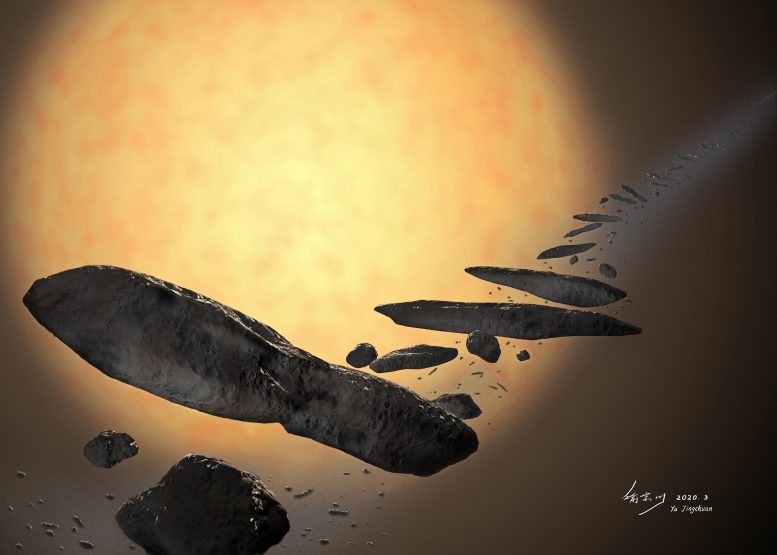

Artist’s impression of the H Oumuamua formation based on ZHANG and Lin’s Cenary. Credit: YU Jingchuan of the Beijing Planetarium
What is the origin of the famous interstellar object ‘Oumuamua? How did it form and where did it come from? An article published on April 13, 2020, in Astronomy of nature by ZHANG Yun of the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) and Douglas NC Lin of the University of California, Santa Cruz, offers a comprehensive first response to this mystery, involving tidal forces such as those felt by the Earth’s oceans and explains all the unusual characteristics of this interstellar object.
Um Oumuamua was discovered on October 19, 2017 by the Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System 1 (Pan-STARRS1) located in Hawaii. As the first known interstellar object to visit our Solar System, ‘Oumuamua bears no resemblance to anything else in the Solar System. Its dry surface, unusually elongated shape, and puzzling movement even led some scientists to wonder if it was an alien probe.
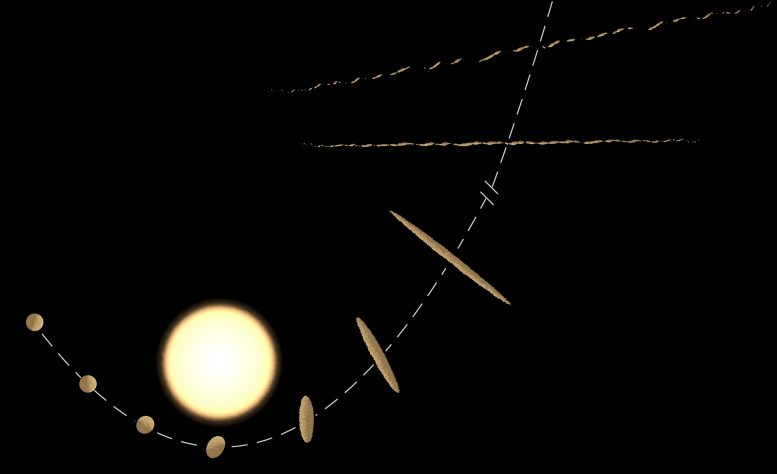

This illustration shows the tidal disruption process that can result in Oumuamua-like objects. Credit: NAOC / Y. Zhang
“It really is a mystery,” said ZHANG Yun, the study’s first author, “but some signs, such as its colors and the absence of radio emission, point to‘ Oumuamua being a natural object. ”
“Our goal is to come up with a comprehensive scenario, based on well-understood physical principles, to put all the tantalizing clues together,” said Douglas Lin, co-author of the study.
In general, the first interstellar object discovered was supposed to be an icy body, like comets. In effect, frozen objects are constantly ejected from their host systems. They are also much more visible due to their apparent coma. However, seca Oumuamua’s dry appearance, similar to rocky bodies, such as asteroids in the Solar System, indicates a different ejection scenario.
“The discovery of‘ Oumuamua implies that the population of rocky interstellar objects is much larger than previously thought. On average, each planetary system should expel a total of around one hundred trillion objects like ‘Oumuamua. We need to build a very efficient scenario, “said ZHANG. “In space, some objects occasionally get very close to a bigger one. The tidal forces of the largest can disrupt these little ones, like the things that happened to Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 when it passed nearby Jupiter. ”
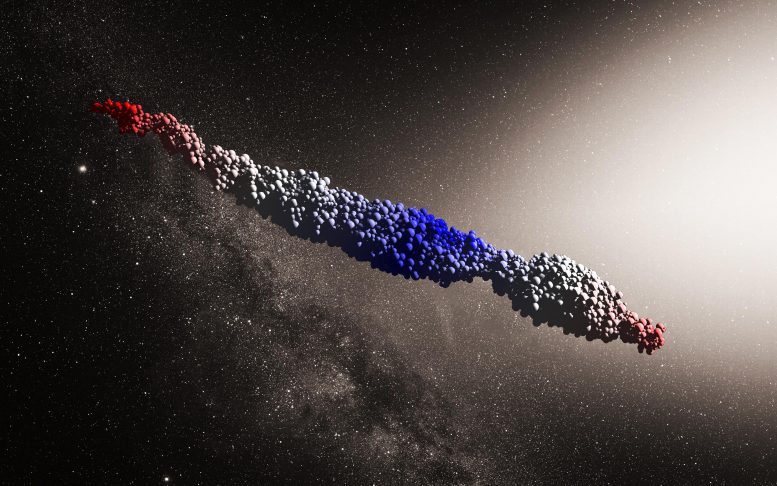
A ‘Oumuamua type object produced by a simulation of the tidal disruption scenario proposed by Zhang and Lin. Credit: NAOC / Y. Zhang (Background: ESO / M. Kornmesser)
ZHANG and Lin performed high-resolution computer simulations to model the dynamics of an object that flies close to a star. They discovered that the star can dramatically divide the object, if it gets close enough to the star, into extremely elongated fragments, and then eject them into interstellar space.
“The elongated shape is most compelling when we consider the phase transition of the material during the stellar encounter. The long axis to short ratio may be even greater than ten. “ZHANG said. Due to intense stellar radiation, the surfaces of the fragments melt at a very short distance from the star and re-condense at greater distances. Like melting chocolate grains, the surface materials come together to keep the shape elongated.
“Heat diffusion also consumes large amounts of volatiles. These fragments become dry and have a surface similar to Oumuamua. “ZHANG added.” However, some water ice buried below the surface may be conserved. These residual water ices could be activated during their passage through the Solar System to cause its non-gravitational movement. “
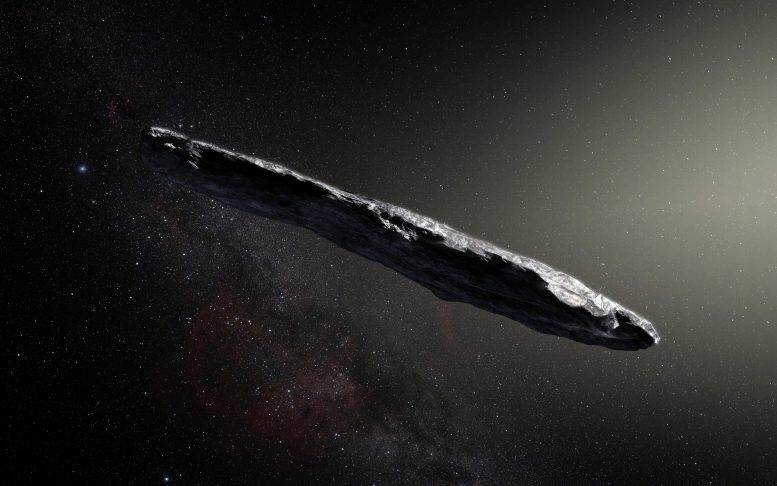

An artist’s impression of ua Oumuamua. Credit: ESO / M. Kornmesser
“The tidal fragmentation scenario not only provides a way to form a single‘ Oumuamua, but it also represents the vast population of rocky interstellar objects. ” ZHANG said. Their calculations demonstrate the efficiency of stellar tides in the production of this type of object. Prospective parents, including long-period comets, debris disks, and even planets, can transform into pieces of ‘Oumuamua during stellar encounters. The inferred numerical density of interstellar objects is consistent with the occurrence rate of ‘Oumuamua.
This work highlights the prolificity of the population of interstellar objects – such as Oumuamua among stars. Since these objects pass through the domains of habitable zones, the possibility of transport of matter capable of generating life by these objects cannot be ruled out.
“This work provides a plausible narrative that links its strange properties to the planet formation process that is ubiquitous in the Milky Way Galaxy, “said Gregory Laughlin, professor of astronomy at Yale University.
”‘ Oumuamua is just the tip of the iceberg. We anticipate that many more interstellar visitors with similar features will be discovered by future observation with the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory, ”Lin said.
“This is a very new field. These interstellar objects could provide critical clues to how planetary systems form and evolve, and how life on Earth began, “said ZHANG.
“This work does a remarkable job of explaining a variety of ‘Oumuamua’s unusual properties with a single, consistent model,” said the US Naval Academy astronomer. USA Matthew Knight, co-leader of the Oumuamua International Institute of Space Sciences team, “As future interstellar objects will be discovered in the coming years, it will be very interesting to see if any exhibits properties similar to Oumuamua. If so, it may indicate that the processes described in this study they are very widespread. ”
Read Oumuamua of Mysterious Interstellar Object Explained by New Formation Theory for more information on this study.
Reference: “Tidal Fragmentation as the Origin of 1I / 2017 U1 (‘ Oumuamua) “by Yun Zhang and Douglas N. C. Lin, April 13, 2020, Astronomy of nature.
DOI: 10.1038 / s41550-020-1065-8
[ad_2]