
[ad_1]
V. Vasiliauskas affirmed that every inhabitant must take charge of the public debt.
“It just came to our attention then. If public debt increases, economic growth decreases, then the amount of public finances that is spent on debt service increases and then there is simply less money left for other areas.
As with family finances, if you borrow, the part of family finances used to pay off debt and pay interest is higher when the situation changes (especially if interest rates rise). Then you have to reduce your other expenses, ”he explained.
On Monday, V. Vasiliauskas presented an overview of the Lithuanian economy and the latest forecasts.
“We can and must use this fragile respite in such a way that we allocate state funds and the support package planned by the European Union to mitigate the effects of the pandemic by intentionally planning long-term investments to transform the economy and solve long-standing problems.” said V. Vasiliauskas.
The central bank director announced better forecasts for this year.
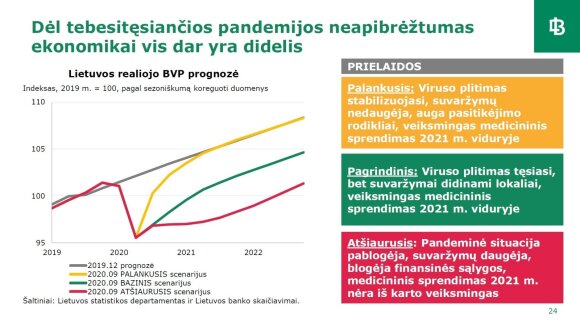
According to the economists of the Bank of Lithuania, in the case of the main scenario, the economy will contract by 2% this year. The economic recession is expected to be less than in 2020 and the projected recovery in 2021 will be more moderate, with GDP expected to grow by 3.1% next year. However, the uncertainty about the consequences of the pandemic for the economy remains high, which is why the Bank of Lithuania has evaluated the harsh scenario so much: in 2020, GDP will contract by 2.4 percent, and next year it will not grow, and the favorable scenario will be -0.2 and +5 percent, respectively. in the report.
In June, Lithuania’s GDP is forecast to contract by -9.7 percent in 2020 and grow by 8.3 percent in 2021.
In summary, the Lithuanian economy has so far suffered less from the pandemic than most countries due to the relatively low prevalence of the virus, the relatively minor economic recession of Lithuania’s main trading partners, the favorable industrial structure, the rapid recovery. consumption and the stimulus measures implemented.
According to V. Vasiliauskas, the better-than-expected economic development during the impact caused by the pandemic was influenced by the relatively minor economic recession in Lithuania’s main trading partners, fewer restrictions on manufacturing activity, relatively small impact on the labor market of the tourism sector.
The economy has also been boosted by public finances, monetary policy, and additional regulatory measures.
Unemployment, inflation and debt
Although the job market is relatively good, it is reported that it has also been affected by the pandemic.
“The number of employees has been increasing since June, but there are still many fewer than a year ago. Wages, although they continued to rise, were much slower than before. The high level of unemployment was determined not only by economic development, but also by government decisions; registered unemployment had already stabilized in June, but was driven by the introduction of job search benefits. In the case of the main scenario, the unemployment rate is expected to reach 8.8% this year, and the average salary will rise by 6.8% ”, predict the economists of the Bank of Lithuania.
According to them, inflation is currently and will be low in the near future: under the main scenario, prices will rise 1 percent this year and 1.2 percent next.
“A large part of inflation is due to even more expensive services, although their prices are rising more slowly. Managing the budget deficit and public debt is becoming increasingly important for the economy to withstand the impact of the pandemic better. than expected, “the report said.

Looking at this year’s budget deficit, we forecast it to be one of the largest since the data was released, with the debt level increasing by 10%. the points will approach 50%. GDP will be the highest in Lithuania’s history.
“For this reason, it is crucial to spend public funds in a rational, thoughtful, purposeful and measured way, both for short-term economic stimuli and for longer-term investments, such as 6.3 billion euros for the DNA plan for the economy future, “warn central bank economists.
The report states that once “fire fighting” ceases, the main criterion for long-term investment should no longer be speed, but quality of projects. One-time “feed” payments may be required at a critical time, but these measures cannot be long-term as they do not address long-standing issues such as low productivity growth, aging population, or regional exclusion. .
“Human capital, that is, educated people with the right skills, is a key factor in transforming the economy to generate the highest long-term returns. However, it is in this direction that the smallest part of the planned financing in the DNA Plan for the Future Economy it is 757 million, 3000 million euros, that is, almost three times less than investment in infrastructure, which is estimated at 2000 million euros.
It is planned to invest 1.4 billion in the development of the digital economy and almost 1 billion in innovation. and measures to combat climate change and energy: 927 million. euros. It is no less important to properly prepare and contract future new EU funds.
Under the Economic Recovery and Resilience Measure, Lithuania is expected to receive 2.4 billion LTL. grants and the country could borrow up to € 3 billion if needed. euros. In order not to miss this opportunity, Lithuania must prepare an ambitious reform plan and ensure that funds are directed to productive areas to create a sustainable and competitive economy in the country, “the report said.
It is strictly forbidden to use the information published by DELFI on other websites, in the media or elsewhere, or to distribute our material in any way without consent, and if consent has been obtained, it is necessary to indicate DELFI as the source.
[ad_2]