
[ad_1]
So far, no official figures have been released on the average real exchange rate in Lebanon, neither from the Banque du Liban, which deals mainly with this matter, nor from external supervisory authorities. However, in recent estimates issued by the International Monetary Fund, some indicators appeared, including economic growth and the size of the gross domestic product … Deconstructing these figures and returning them to what they were in the previous year after reducing the rates of deflation in production, it was shown that the Fund readjusted the value of GDP. According to an exchange rate different from the average exchange rate adopted in recent years (it was 1507.5 pounds on average), that is, the product was calculated on the basis of an exchange rate equivalent to 6000 pounds per dollar and decreased from 52.5 billion to 18.7 billion dollars, accompanied by an inflation rate of 85.5% and a decrease in per capita product. From $ 7,660 to $ 2,740, in addition to a current account deficit of $ 3 billion.
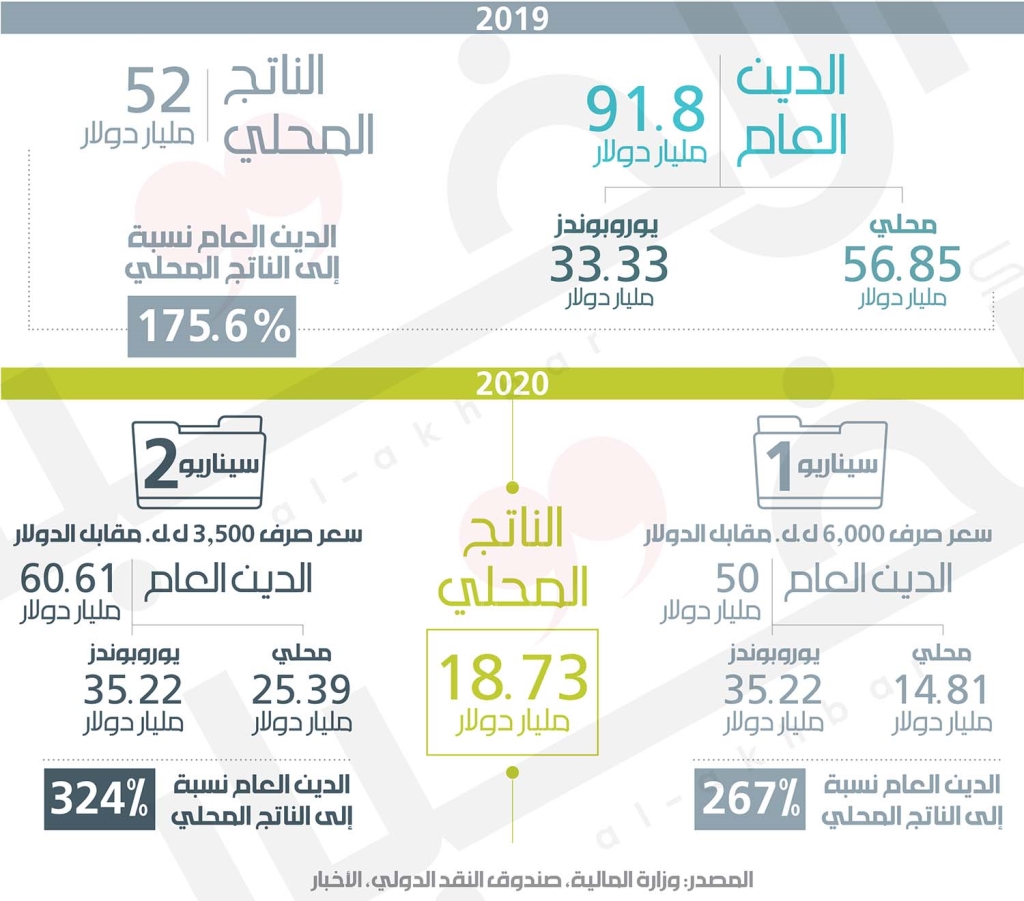
In the event that this figure was officially approved by the fund itself, it should be noted that there is data that indicates that the fund has not yet made its decision on the matter, so it hesitates to recognize the adoption of the exchange rate equal to 6000 lira per dollar, then dealing with the issue of the determination and distribution of losses becomes another matter. . One of the most important standard indicators that the Fund considers essential in any process of restructuring a country’s debt is the debt / GDP ratio, which should not be higher than 100%, but lower. It is recommended that it be 80%. The Fund believes that this indicator is essential to address debt sustainability and the capacity of the state in question to continue to serve it.
So what does it mean to recalculate debt on the basis of an exchange rate of £ 6,000 relative to production?
Last year, the debt-to-output ratio was 175.6%, according to the government’s recovery plan, which the government implemented in cooperation with Lazar and in consultation from under the table with the International Monetary Fund. The plan indicated that the debt-output ratio would gradually decrease to 102% in 2020 and reach 99.2% in 2024. At the same time, the dollar exchange rate would increase from 1,507.5 liras on average to 3,500 liras in 2020 and 4,082 lire in 2023 and lire 4,297 in 2023. The year 2024. Of course, this matter is calculated on the basis of a 75% deduction on Eurobonds and 40% on Lebanese pound bonds, in addition to a set of other indicators calculated to correct the balance of payments (mainly correcting the current account), and studying the viability of government revenues and expenditures to continue financing the deficit.
At the time, the value of Eurobonds was $ 31.3 billion (with interest earned today, which was not paid, increased by $ 2.2 billion), and there is about $ 3 billion in debt with countries or international organizations, in addition to debts issued by bonds. Lebanese pounds worth 84,701 million pounds, which also increased by a value of 2,100 million dollars. In total, the value of the debt was equal to 142 billion pounds ($ 94.19 billion) at the end of August 2020 without any deductions and without reassessing the price of the dollar against 135.946 million pounds (90.1 billion dollars) at the end of 2019 when GDP equaled 79,173 million pounds. ($ 52 billion), except that after calculating the new exchange rate, which is 6000 lira to the dollar, and after the big drop in the value of production, the debt / production ratio will be higher than 267% and therefore the deduction rate will be much higher to reduce the debt / debt ratio. Production is less than 100%, and if we follow the government’s plan to deduct the debt (70% on the Eurobond and 40% on the internal debt), we will still have a debt of 19,430 million dollars, or 103% of GDP .
This issue will not only have a significant impact on this percentage, but will have a greater impact on the size of subsequent losses in the Banque du Liban budget and in the budgets of the banks. The larger this currency gap, the greater the effect of the exchange rate revaluation. The dollar demanded by the banks from the depositors was their price, for example 1507.5 lire, then now it is paid on the platform specified price of 3900 lire, but 6,000 lire will be paid if this price is adopted when unifying the rates requested by the International Monetary Fund as a basic and prior condition for any program with it. The fund’s dollar loans are originally tied to the fund’s pre-conditions.
Subscribe to «News» on YouTube here