[ad_1]
The mineral “lithium” is available in relative abundance. It is ranked 25th in terms of abundance on the list of elements on the periodic table of natural elements. It is lightweight and has a strong affinity for high reactivity. Cost of sale related to the cost of extracting it from salt water or rock. Last year, the world produced around 77 thousand metric tons of this mineral, but there are high expectations that demand for it will increase in the coming years in line with the high rates of technological production and its development, which will cause a shortage of the quantity supplied in the market.
What increases the risk of supply shortages is that the extraction of “lithium” is a complicated, expensive and time-consuming process. The brine is extracted under a salt crust that forms due to natural factors and is placed in special pools exposed to the sun and air for evaporation. The result of this process is subjected to a crystallization process that aims to extract the other salts in the remaining solution. After that, the product is purified and finished with a concentrated “lithium” solution.
69,000
The price of a metric ton of lithium metal traded on international stock exchanges, which is 25% lower than its price in the past Q1
The second way to extract it is no less difficult and complicated. It is present in the structure of solid rocks, which are crushed and “roasted” with the aim of turning them into powder. Subsequently, the powder is subjected to a series of roasting after adding substances, such as sulfuric acid and black ash, until the refining and purification process is carried out to obtain a substance with a high concentration of “lithium”. Currently, laboratories of production companies around the world are working on the use of new materials in the extraction process to save a significant part of the production cost through lower temperatures sufficient to complete the roasting process (the used part of the rock ).
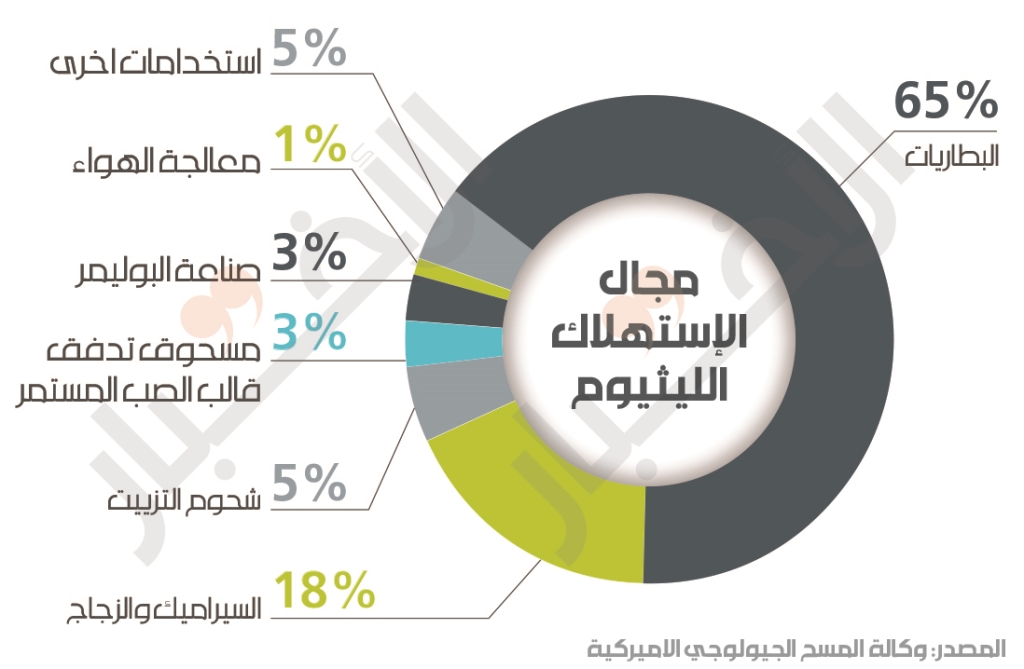
This metal is used primarily to make batteries. This destination acquires 65% of annual production, but has other uses such as ceramics and glass, which account for 18% of production, fats consume around 5% and the polymer industry 3%.
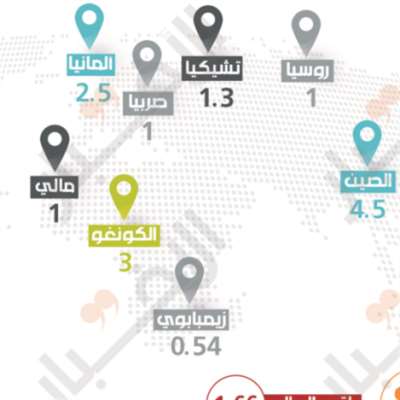
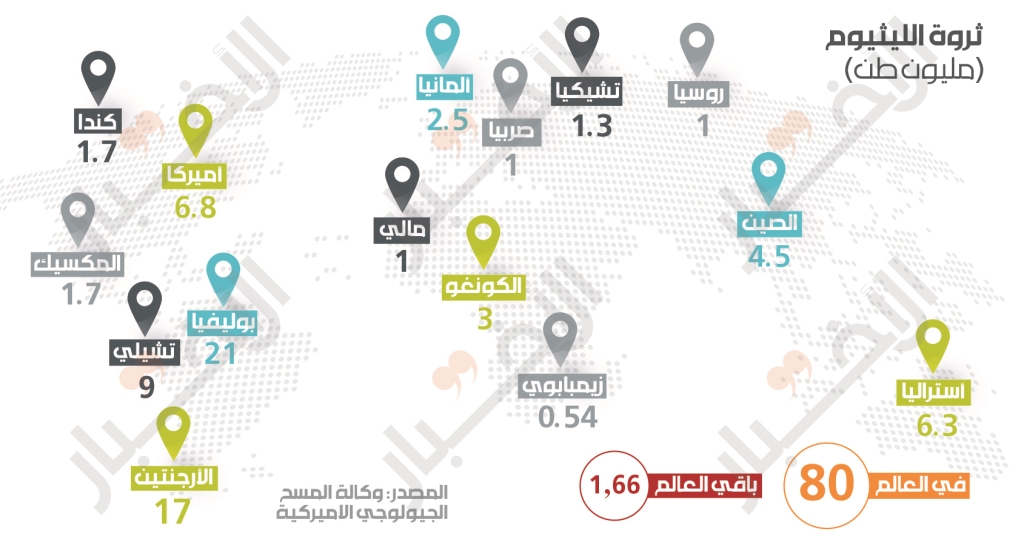
The largest reserve of unextracted lithium is in Bolivia. The quantity available for extraction is estimated to be 21 million tons, followed by Argentina, which stores around 17 million tons, Chile with 9 million tons and Australia with 6.3 million tons. In total, the USGS estimates that 80 million tons have yet to be mined.
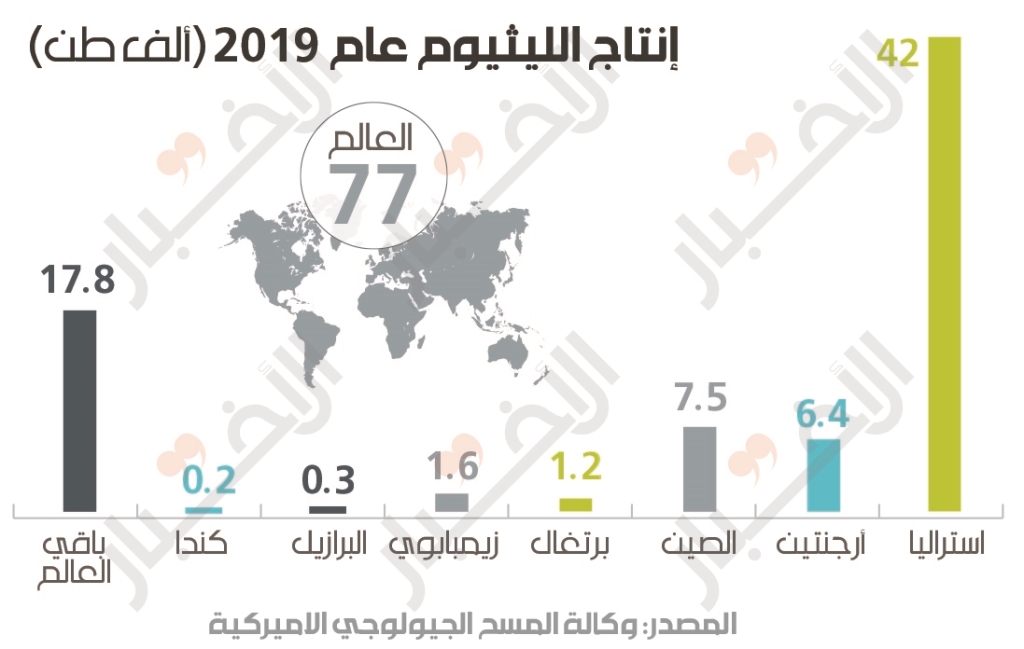
But in terms of extraction volumes, Australia ranks first. Last year, its production reached 42 thousand tons. While the quantity produced in Argentina was about 6,400 tons, and China was 7,500 tons.
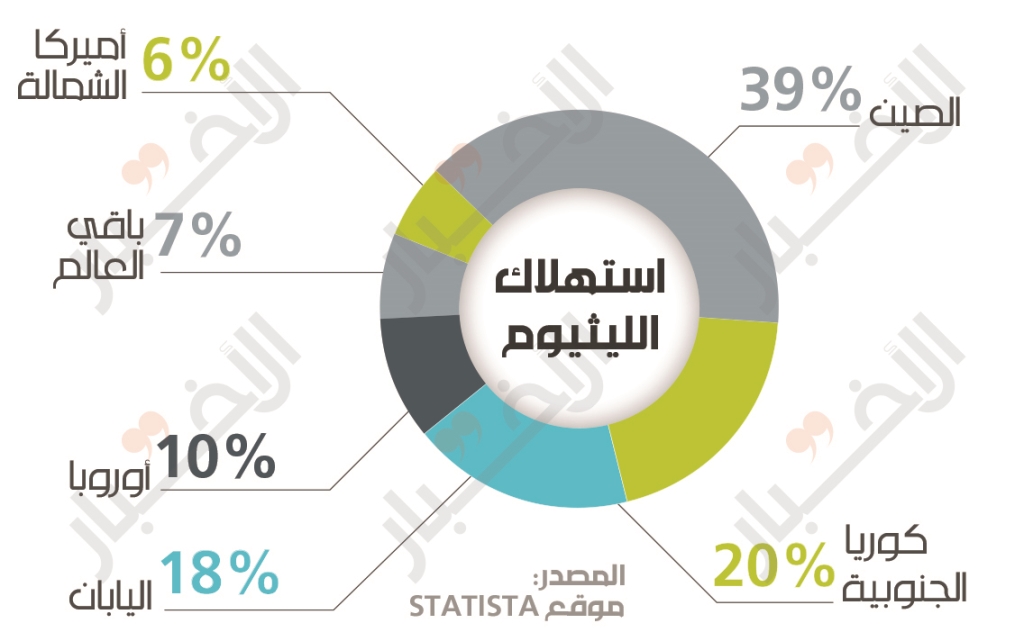
On the consumption side, statistics indicate that China is the largest consumer of this mineral. Its market share is 39% of world production. This is due to China’s production policies in high value-added technological goods. It has made a strong entry into the field of lithium battery manufacturing and has acquired a large part of the world market. According to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, a research firm in London, out of 136 companies that make lithium batteries, 101 are based in China. China’s fate is most evident in its investment in lithium mining and manufacturing. The Chinese company Tianqiu Lithium recently bought $ 4 billion in shares of SQL, which is one of the largest lithium producers in Chile. Thus, the Chinese company became the second largest shareholder of the Chilean company, noting that this Chinese company owns 51% of the largest lithium field in Australia. Furthermore, the Chinese company has relative control over the production and manufacturing stages, which means it has a hand that extends to the entire supply chain for the lithium battery industry and also to its sales market.
Chinese acquisitions of production and manufacturing lines are a cause for concern in the United States. The future of energy and associated technological production around the world depends on battery technology. If China continues with this control, US companies that produce goods that require rechargeable batteries will be relatively under the control of Chinese companies. The level of risk increases as the level of dependence on this type of battery doubles. As an indication, the coup in Bolivia was directly linked to the conflict over the white oil mines in Bolivia. The latter has the largest arsenal in the world. The owner of the company “Tesla” that makes electric cars (the issue of lithium metal and its prices is one of the biggest concerns of the company) Elon Musk expressed broad interest in the issue of the coup in Bolivia, and tweeted the past month of July saying: “The United States can strike wherever it wants, and you have to.” Accept the topic.
Click on the chart to enlarge it
Subscribe to «News» on YouTube here