[ad_1]

2020/12/13 10:11 Weather News
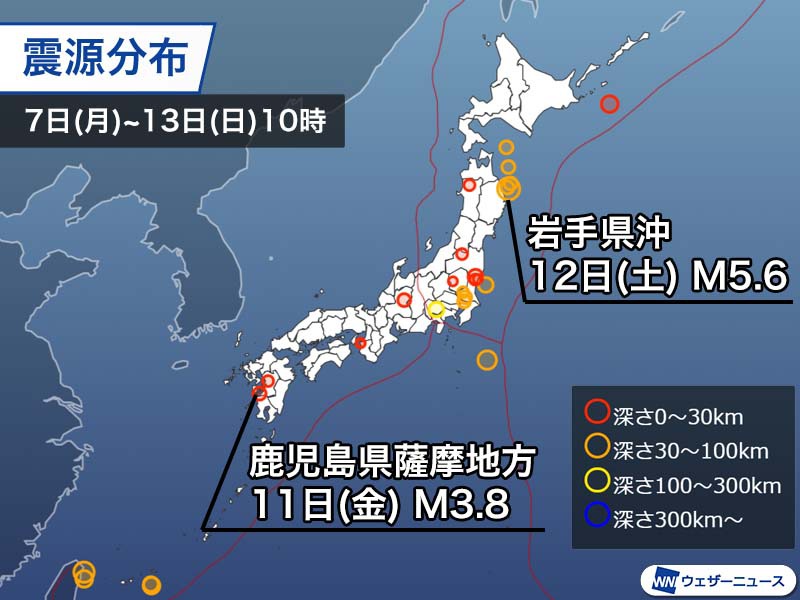
Last week, the number of earthquakes observed in Japan has been at the same level as the previous week. There have been two earthquakes with a seismic intensity of 3 or more, and a seismic intensity of 5 less has been observed in Aomori Prefecture. The number of earthquakes increased from Kanto to the Pacific side of northern Japan. (Added from December 7 to December 13 at 10:00)
In this earthquake, 15.2 seconds after the detection of the seismic wave, a tremor with a seismic intensity of approximately 5 minus was expected in the Sanpachi-Kamikita region of Aomori Prefecture, for which a bulletin has been announced earthquake emergency (warning). According to the analysis of the Meteorological Agency, it is a reverse fault type mechanism with an east-west axis of pressure.
It was the earthquake off the east coast of Aomori prefecture on December 19, 2019 that caused a tremor with a seismic intensity of 5 less or greater in Aomori prefecture, as we observed a seismic intensity of 5 less in the same upper town as this time. This year, the earthquake with a seismic intensity of less than 5 observed in Japan is the fifth since the earthquake off the coast of Ibaraki prefecture on November 22.
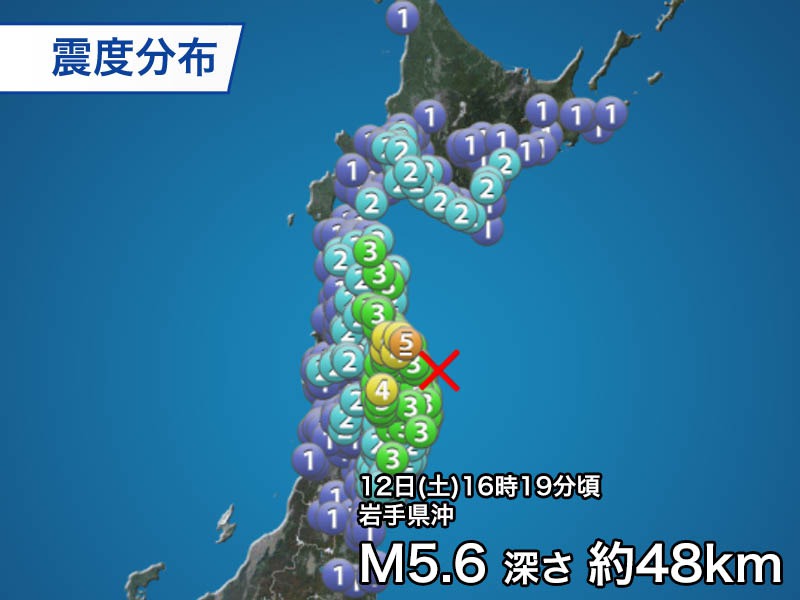
The area from Iwate prefecture to eastern Aomori prefecture is one of the areas where seismic activity has been active since the Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011. On February 17, 2015, it was produced an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.7 in the same center as this time, and a seismic intensity of 5 higher was observed in Hikami-cho, Aomori prefecture, and a seismic intensity of 5 lower in Fuyo-mura, prefecture of Iwate.

Although the name of the earthquake center by the Meteorological Agency falls within the area of ”Satsuma region, Kagoshima prefecture”, the actual earthquake center is considered the Yashiro Sea off the coast of Minamata city, Kumamoto prefecture. . This earthquake is the area corresponding to the “Yadakai section” of the Hinagu fault zone that extends from Kumamoto prefecture.
The Hinagu fault zone is adjacent to the Futagawa fault zone in Kumamoto prefecture, and part of it is believed to have been active during the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake. The Hinagu fault zone is large and can be divided in “Takano-Shirahata section”, “Hinagu section” and “Yayokai section”. According to the government’s Earthquake Research Promotion Headquarters, an earthquake with a magnitude of about 7.3 will occur with a probability of 0 to 16% within 30 years in the “Yayokai section” near the place where the earthquake occurred this time. . Although the activity of the Kumamoto earthquake has been slow, it seems necessary to be aware of the earthquake in the area of the Hinagu fault.

In this earthquake, there was a tremor equivalent to seismic intensity 4 in the local seismic intensity class, mainly in the northern part of Taiwan near the source of the earthquake. Also in Japan, we have observed tremors with a seismic intensity of 2 in Yonakunijima and Ishigakijima. Although the scale of the earthquake was large, it was a shallow one, about 70 km deep, and fortunately did not cause great damage.
The seismic intensity class in Taiwan was 8 classes from 0 to 7 until last year, but as of this year 2020, it has been changed to 10 classes that divide the seismic intensity into 5 minor, 5 strong, 6 weak, 6 strong like in Japan. .. This earthquake was the largest this year, but the maximum seismic intensity was only 4, and no tremors equivalent to the recently established seismic intensity of 5 lower or higher were observed in the new seismic intensity class.
* Information on the source and intensity of seismic intensity in Japan comes from the Meteorological Agency, unless otherwise stated. Information on overseas earthquake sources comes from the US Geological Survey (USGS), unless otherwise noted. Source information may differ depending on the issuing organization.



