
[ad_1]
02/21/2021 10:22 AM Weathernews
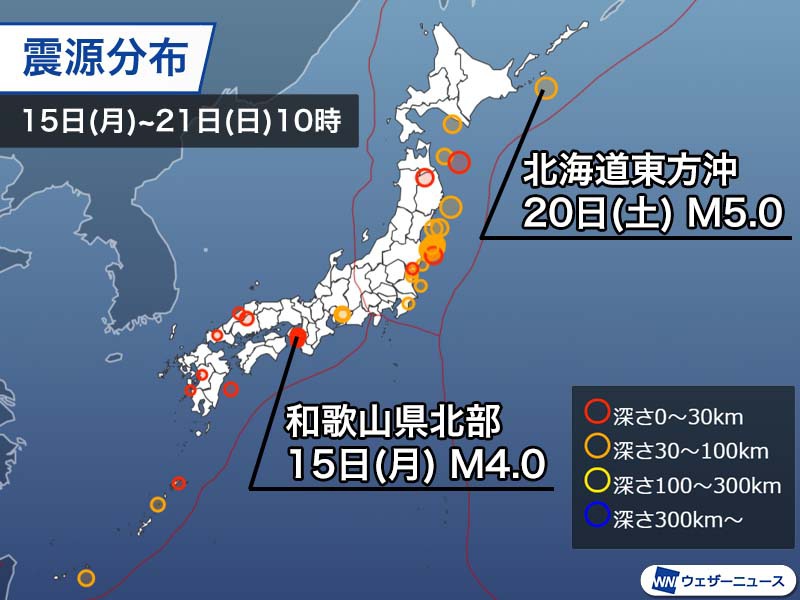
Last week, the number of earthquakes observed in Japan is not as high as the week before, which was affected by the earthquake off Fukushima prefecture, and there have been eight earthquakes with a seismic intensity of 3 or more . (Added from February 15 to 21 at 10:00)
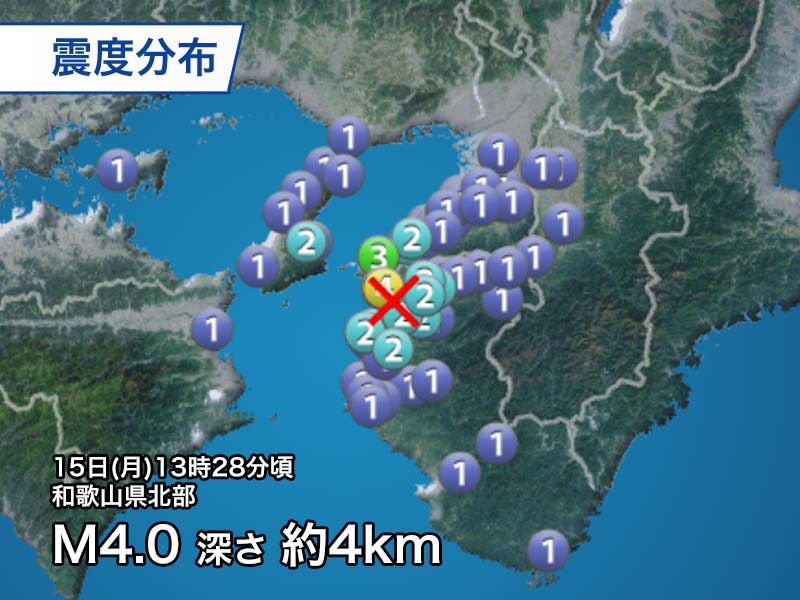
This is the first earthquake in eight years since June 2013 with a seismic intensity of 4 or more and originated in the northern part of Wakayama prefecture. The earthquake mechanism is a type of reverse fault with a pressure axis in the west-northwest-east-southeast direction, and the strike component is slightly large.
Although there are no known active faults in northern Wakayama prefecture, seismic activity is active due to the difference in subduction angle of the Philippine Sea plate and the influence of geology. The magnitude of around 5 occurs frequently, and the depth of the epicenter is very shallow, less than 10 km, as in this earthquake, so the shaking can be large. Recently, in July 2011, a 5.5 magnitude earthquake occurred slightly south of the epicenter, with a maximum seismic intensity greater than 5.

The largest aftershock was a magnitude 5.5 that occurred at 9:26 p.m. on Monday the 15th, and two other earthquakes of magnitude 5 or more occurred. Although aftershock activity has subsided, earthquakes of magnitude 4 and above occurred on Friday the 19th and Saturday the 20th, and there is still a high possibility of an earthquake with a seismic intensity of about 3.
In addition, the Government Headquarters for the Promotion of Seismic Research foresees the occurrence of similar types of earthquakes along the Japan Trench, called “submerged plate earthquakes” and “smaller interplate earthquakes” as in Fukushima prefecture. . The probability that an earthquake with a magnitude of 7 to 7.5 will occur in the next 30 years is as high as 26% or more, so it is safe to think that an earthquake of the same level as this moment will come at any moment and be prepared. .

A 6.2 magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of Vanuatu in the South Pacific on Tuesday, Japan time. Although the depth was very shallow, about 6 km, there were no strong shaking on the islands and no damage was caused.
The area around Vanuatu is an earthquake-prone area on the border between the Australian and Pacific plates. At the same boundary, there was a large earthquake with a magnitude of 7.7 on Wednesday the 10th and a tsunami was observed in Vanuatu. The earthquake mechanism is analyzed as a type of reverse fault with an east-west axis of pressure.
Also, although the scale is a bit small, on Thursday the 18th a magnitude 5.6 earthquake occurred in the southwestern part of Iran. Since it was an earthquake on the ground, strong tremors occurred around the epicenter and injuries have been reported.
* Information on the epicenter and seismic intensity in Japan comes from the Japan Meteorological Agency, unless otherwise noted. Information on overseas epicenters comes from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) unless otherwise noted. The epicenter information may differ depending on the issuing organization.




