[ad_1]
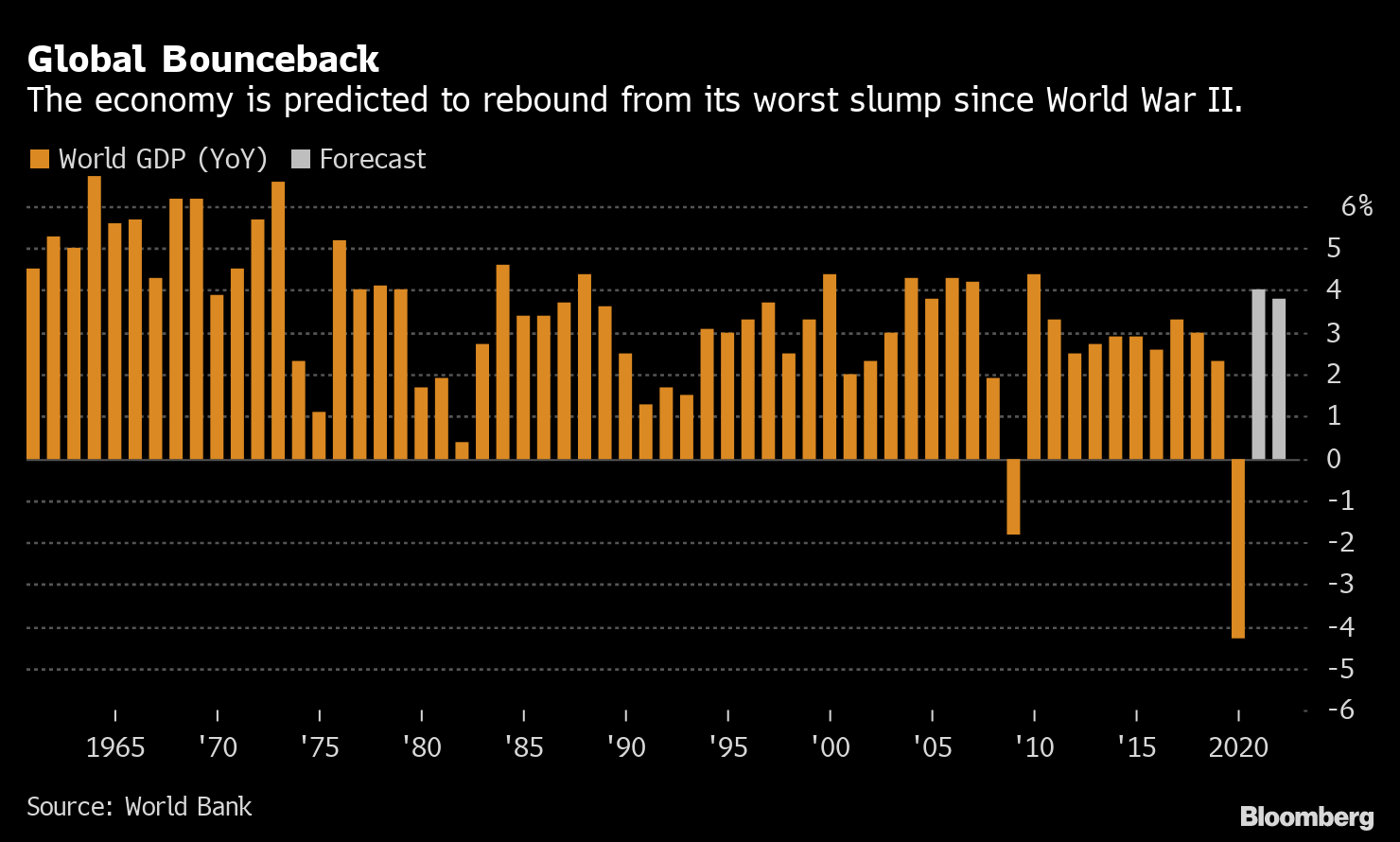
The recovery of the world economy this year from the most severe recession after World War II is expected to be slightly slower than expected due to the re-expansion of new coronavirus infections in developed countries. The forecast was made in the semi-annual World Economic Outlook (GEP) report released by the World Bank on the 5th.
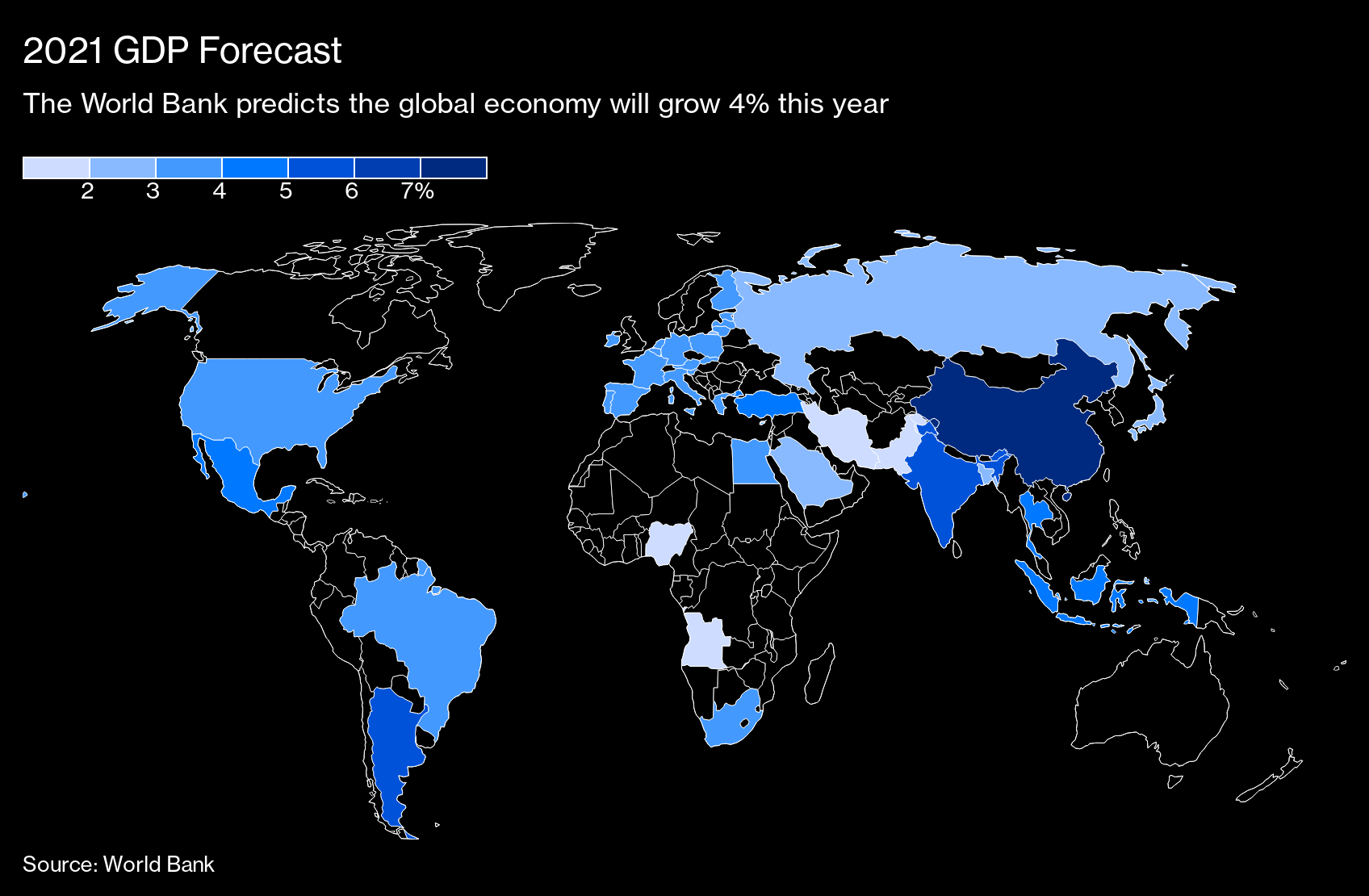
The growth rate of the world economy in 2021 is expected to be 4%, which is lower than the forecast (4.2%) as of June last year, and is expected to grow by 3.8% in 2010. The World Bank has revised their growth forecasts for the US and the euro zone were lowered, raising China’s growth rate by 1 point to 7.9%.
The World Bank, which expects a 20-year growth rate of minus 4.3%, notes that the prospects for short-term economic recovery are accompanied by “extraordinary uncertainty.” Unless governments improve the business environment, education and productivity, the new Crown pandemic could reduce the growth rate of the world economy over the next decade.
In the preface to the GEP, Governor Malpas said: “The policies that are trying to boost the current fragile economic recovery and ensure strong growth are public health, debt management, politics and the budget structure. we face a great challenge in the area of reform. “
Global rebound
The economy is projected to rebound from its worst recession since World War II.
Source: World Bank
According to the World Bank, millions of people have fallen into poverty due to the Corona disaster, and about a quarter of emerging and developing countries have lost at least 10 years of income growth, but the positive effects of vaccination . Confidence, consumption and trade are expected to boost this year and next.
However, he said that there are still many risks in the outlook, and mentioned the spread of new infections, delays in vaccination, financial straits due to large debts, unemployment and prolonged suspension of business activities. Was. He also warned that a prolonged economic downturn could trigger bankruptcy and trigger a financial crisis.
Bouncing
Emerging markets will continue to outperform advanced economies
Source: World Bank.

The World Bank also analyzed that the share of total national production (GDP) of government loans from emerging and developing countries in 20 years is likely to have increased by 9 points, the highest since the debt crisis in late 1990. the 1980s. He called for society to cooperate to reduce the burden of debt.
He also predicted that this year’s growth rate for emerging and developing countries will be 5%, while explaining that the improvement mainly reflects the recovery of China, where the new krone is almost suppressed. With the exception of China, pandemics will continue to affect consumption and investment, and the growth rate of emerging and developing countries is expected to remain at 3.4% this year and 3.6% next year.
GDP forecast 2021
The World Bank predicts that the world economy will grow 4% this year
Source: World Bank.

Other main points of GEP are as follows.
- The 21-year US growth forecast has been revised down from 4% to 3.5%. New restrictions and the widespread re-expansion of infections are expected to curb demand early in the year
- Due to the severe lockdown (city lockdown), the projected growth rate for the euro area has fallen from 4.5% to 3.6%. The tourism industry is likely to continue to decline
- The growth forecast for Central and South America was raised from 2.8% to 3.7%. The background is the relaxation of restrictions, the acceleration of vaccination in the second half of the year and the prospect of an increase in the prices of crude oil and metals.
Original title:The global economic outlook is dimmed by the increase in viruses before vaccines