[ad_1]
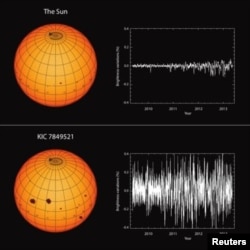
A new study suggests that the sun appears to experience far fewer changes in brightness and intensity than other stars like this one.
The researchers reported last week on their 369-star exam. They compared each to the sun in terms of surface temperature, size, and rotation. They found that, on average, the other stars were five times brighter variability that our sun
A report on the study and its findings was published in Science magazine.
The Lead Author was Timo Reinhold, an astronomer at the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Germany. He told Reuters news agency that the variability in brightness results from dark spots on the surface of the star moving in and out of see.
“A direct measure of solar activity is the amount of sunspots on the surface,” Reinhold said. “Find such stars with very similar parameters like our sun, but being five times more variable was surprising. “
The sun, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, is an average-sized star that formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. It stretches about 1.4 million kilometers across and has a surface temperature of 5,500 degrees Celsius.
The researchers compared scientific data on similar stars with historical records of the sun’s activity. The records included about 400 years of observational data on sunspots. The researchers also studied about 9,000 years of data based on variations of chemical elements in tree rings and ice accumulation linked to solar activity. These records show that the sun has not been much more active than it is now.
The researchers said that increased magnetic activity related to sunspots can lead to electromagnetic events affecting the Earth. For example, large plasma releases, a collection of charged particles, from external areas of the sun’s atmosphere could cause problems for satellites and other communications equipment. Other electromagnetic activities could also lead to such difficulties.
The discovery that the sun does not undergo as many changes as other stars may be good news for life on Earth.
A much more active sun could have had more important effects on Earth. geology and ancient climate. An “overly active” star would definitely change the living conditions on the planet, so living with boring the star is not the worst optionReinhold said.
The findings, he noted, do not rule out the possibility that the sun is in a quiet period and could become more variable in the future.
However, the researchers say there are no signs that solar activity is going to increase anytime soon.
“For the last decade, the sun has been quite weakly active, even at its own low level rulesThey said in a statement. “Activity predictions for the next 11 years indicate that this will not change anytime soon.”
I’m Bryan Lynn
Reuters reported on this story. Bryan Lynn adapted the report for VOA Learning English, with additional information from the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research. George Grow was the editor.
We want to hear from you. Write us in the Comments section and Visit our facebook’s website.
________________________________________________________________
Words in this story
rotation – north. turning in a circular direction
variability – north. the state of change often
Author – north. a writer of a book or report
see – n. the ability to see something or be seen
parameter – north. a limit that controls how something is done
geology – north. The study of rocks and soil and the physical structure of the Earth.
boring – adj. it is not interesting
option – north. an option or possibility
decade – north. a period of 10 years
standard – north. a level of quality or behavior