
[ad_1]
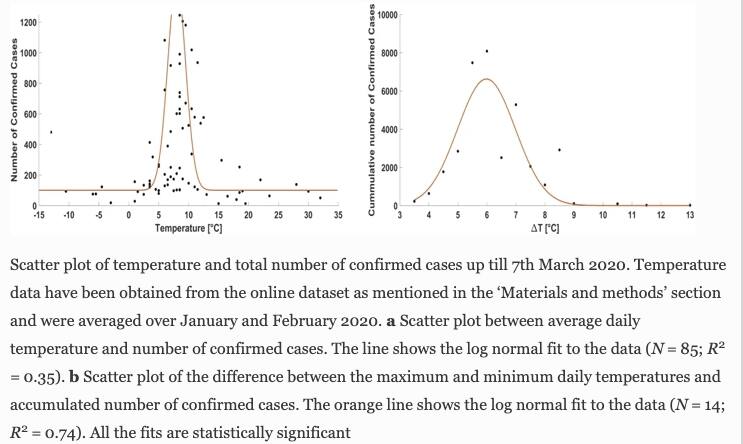
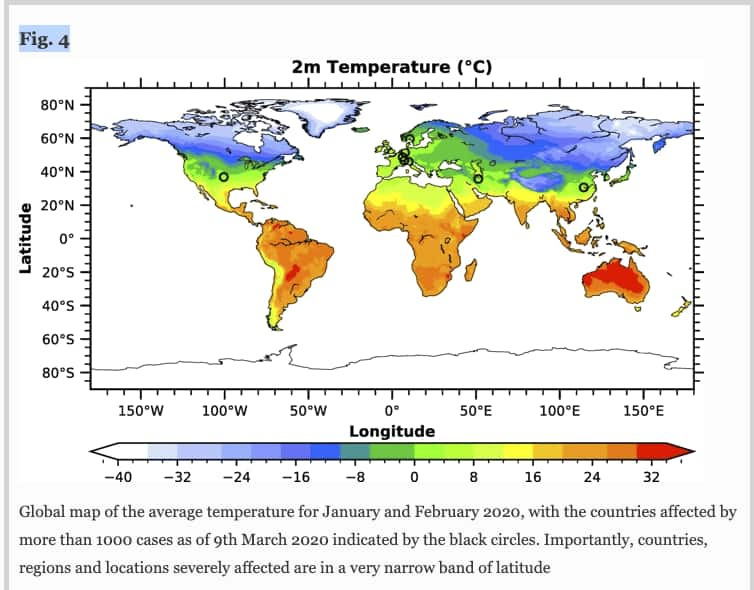
New Delhi: A recent study by a team of IIT-Madras researchers found lower cases of COVID-19 in regions with high temperatures. Data collected from around 85 locations shows that 90% of confirmed coronavirus cases were reported in the region with temperatures ranging from 3 ° C to 12 ° C.
For the study, the researchers saw more than 1.07,351 confirmed cases from 85 locations worldwide, including highly affected provinces in China, South Korea, Italy, France, Iran, Germany, the United States, Spain, and Japan. These data were further analyzed on meteorological parameters.
The reports also suggested that there is a very strong relationship between the UV index and the number of confirmed cases. In areas where the UV index was greater than 5, the number of confirmed infected cases decreased further. Higher temperatures or prolonged exposure to UVC radiation have been documented to decrease virus infectivity.
The study also suggested that artificial UV radiation could be one of the effective ways to sterilize accumulated environments to reduce the spread of the virus among the community.
Previous studies suggest that the most common influenza viruses are seasonality, which implies that during colder temperatures, influenza caused by viruses increases, which then decreases with warming air temperatures. Although, this assumption so far has not been supported by any robust analysis and scientific research.
Professor Sachin S Gunthe from the IIT-Madras Department of Civil Engineering in his previous studies has shown that the survival of other influenza viruses has reduced exposure to high temperatures and a higher UV index. However, this study is based solely on statistical evidence. There is no physiological evidence to prove this fact.
[ad_2]