[ad_1]
Updated: May 8, 2020 10:19:16 am
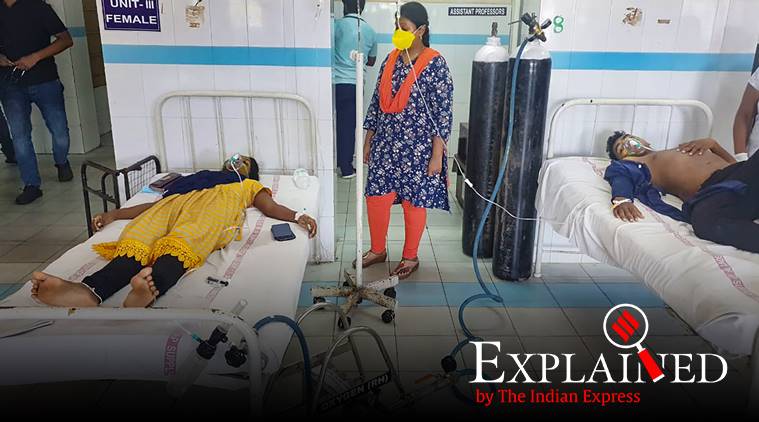
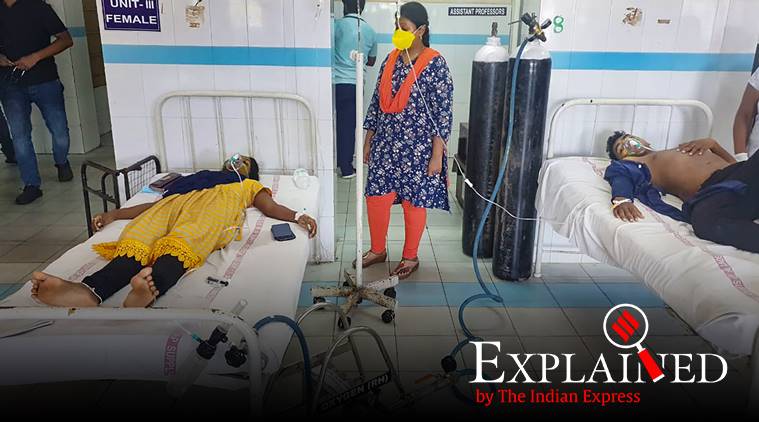 People affected by the styrene gas leak receive oxygen support at the KGH Hospital. (PTI Photo)
People affected by the styrene gas leak receive oxygen support at the KGH Hospital. (PTI Photo)
A gas leak from the LG Polymers factory located on the outskirts of Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, killed at least 11 people on Thursday. The factory was due to reopen on Friday after the shutdown, and gas began leaking as workers prepared to resume work.
The factory is located more than 15 km from the city and the gas leak affected more than 2,000 residents from five nearby villages. While some villagers fled, many fell unconscious on the roads.
The factory, established in 1961, manufactures general purpose polystyrene and high impact polystyrene, expandable polystyrene, and engineered plastic composites.
The law in India provides protection to victims of such chemical disasters. Here is a look at some of these provisions:
At the time of the Bhopal gas tragedy, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) was the only relevant law specifying criminal liability for such incidents, the Legislative PRS reported.
The CBI had initially charged the defendant in the case under Section 304 (wrongful death not equivalent to murder) of the Indian Penal Code (IPC).
The charges were later framed in Section 304A, which deals with wrongful death and imposes a maximum penalty of two years and a fine. The charges were reformulated after a 1996 Supreme Court ruling held that there was no evidence to show that the defendant was aware that such a gas leak would occur and kill people.
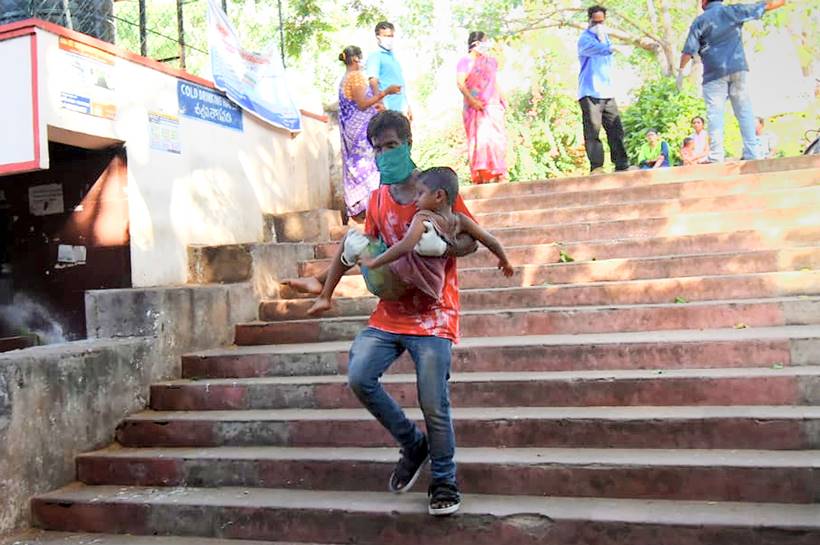 A man rushes to bring his son for treatment at the KG Hospital in Visakhapatnam. (PTI Photo)
A man rushes to bring his son for treatment at the KG Hospital in Visakhapatnam. (PTI Photo)
Shortly after the tragedy, which killed 2,000 people, the government passed a series of laws that regulate the environment and prescribe and specify safeguards and sanctions. Some of these laws were:
1. Bhopal Gas Leakage (Claims Processing) Act, 1985, empowering the central government to secure claims arising out of or related to the Bhopal Gas Tragedy. According to the provisions of this Law, such claims are dealt with quickly and fairly.
2. The Environmental Protection Act of 1986, which empowers the central government to take measures to improve the environment and set standards and inspect industrial units.
3. The Civil Liability Insurance Act of 1991, which is insurance intended to provide relief to people affected by accidents that occur while handling dangerous substances.
4. The National Environmental Appeals Authority Act, 1997, under which the National Environmental Appeals Authority can hear appeals regarding the restriction of areas in which industries, operations or processes or Class of industries, operations or processes will not be carried out or will be carried out subject to certain safeguards under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.

5. The National Green Court, 2010, establishes the establishment of a National Green Court for the effective and expeditious elimination of cases related to the protection of the environment and the conservation of forests.
According to the PRS Legislative, any incident similar to the Bhopal gas tragedy will be tried in the National Green Court and probably according to the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. “… if a company commits a crime , each person directly in charge and responsible will be considered guilty, unless they demonstrate that the crime was committed without their knowledge or that they have exercised all due diligence to avoid the commission of said crime, “says PRS.
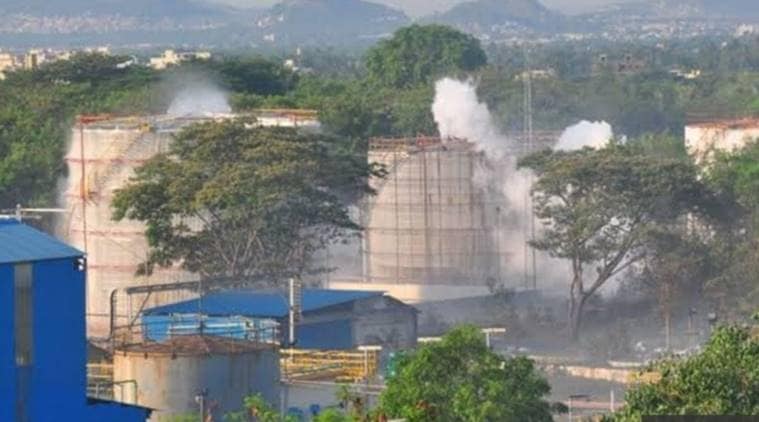 The gas leak was reported at 2.30 am on May 7, 2020. (Twitter / Srijana Gumalla)
The gas leak was reported at 2.30 am on May 7, 2020. (Twitter / Srijana Gumalla)
The state of chemical disaster risk in India
According to the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), in the recent past, more than 130 significant chemical accidents have been reported in the country, resulting in 259 deaths and causing serious injuries to more than 560 people.
There are more than 1,861 Major Accident Risk Units (MAH) distributed in 301 districts and 25 states and three Union Territories in all areas of the country. In addition, there are thousands of registered and hazardous factories and unorganized sectors dealing with numerous ranges of hazardous materials presenting serious and complex levels of disaster risk.

For the latest news explained, download the Indian Express app.
© The Indian Express (P) Ltd
.
[ad_2]