
[ad_1]
After the procedure to declare a city was suspended in the last election years (2018, 2019), and no new city has been opened in Hungary since 2013, this year, in principle, it would have been possible to donate titles. That is not what happened. Orbán’s government apparently
He tightened the government decree regulating the declaration of a city in two steps, and then set a new direction for urbanization, in which cities with county status became the winners and small cities the losers. The Secretary General of the National Association of Local Governments calls for the launch of the Hungarian Small Villages Program, inspired by the Hungarian Villages Program.
The rank of city was awarded by the king or the local landowner in the Middle Ages, but even later the title could be obtained almost everywhere from some higher authority. In some countries, the title may be lost, but there have been few examples of this in Hungary since the transition to civil administration. As a rare exception, the then over ten thousand enthusiastic Mezőkövesd was “demoted” in 1887, that is, declared a large town, and received the title only decades later, in 1973.
Our urbanization rate is western
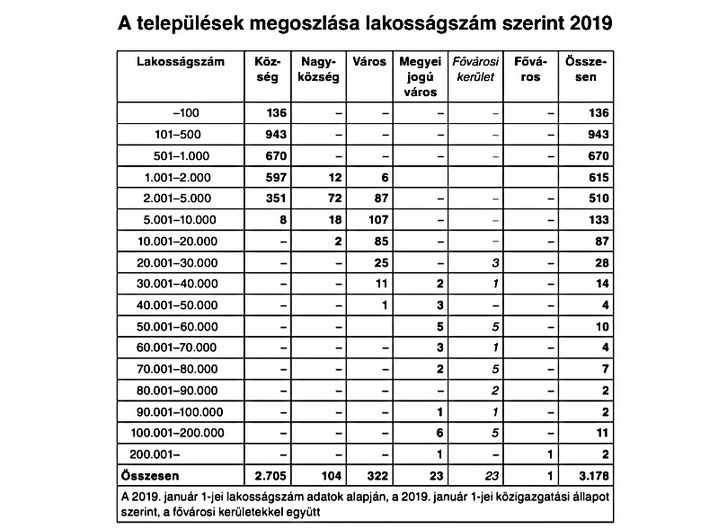
The great commitment of the settlements is not incomprehensible, since the possession of the rank of city has created a privileged situation in all ages. Not to mention that politicians also tried to manage the distribution according to their interests. Today, 346 of Hungary’s 3,178 settlements have urban status and more than two-thirds of the population lives here. The rate of domestic urbanization follows Western rather than Eastern patterns. It is also a Hungarian peculiarity that more than half of the cities were able to move up the administrative ladder as a result of the regime change and subsequent permissive regulation.
Already in the late 1990s, experts sounded the alarm and began talking about the devaluation of the city’s title. However, politics was not interested in criticism at all,
Urban lots were distributed up to between 25 and 30 large municipalities in each electoral cycle.
These include Gönc in Tolna county (1972 inhabitants), Pacsá in Zala county (1576), Őriszentpteres in Vas county (1141) and Pálháza (1034), the smallest and northernmost city in the country.
From the center to the brand
András Trócsányi, head of the department, associated the localities with the title of city after 1990 in five types of settlements.
- The type of spatial structure is the center of a microregion or microregion. For example, Aszód, Csákvár, Jánosháza, Nagybajom, Szentlőrinc or Tiszaföldvár can be included in this group.
- The economic-labor type has become the economic center of its environment with the presence of one or more competitive companies. Some examples are Bábolna, Boly, Répcelak or Sajóbábony.
- The classic tourist town has no catchment area in the traditional sense and is one of the smallest cities in terms of population. The typical representative of the group is Balatonföldvár, Bük, Harkány, Igal, Venice or Zalakaros.
- For image-type cities, the settlement name acts as a brand name. Badacsonytomaj, Herend, Máriapócs, Pannonhalma and Visegrád belong to this group.
- In the case of the agglomeration type, rapid population growth is only followed later by the development of infrastructure. A satellite city of this type is Diósd, Kerepes, Piliscsaba or Veresegyház in the agglomeration of Budapest, Hajdúsámson in Debrecen, Alsózsolca in Miskolc, Sándorfalva in Szeged and Kozármisleny in Pécs.
The Research Group in Positive Psychology of the Faculty of Pedagogy and Psychology of the Eötvös Loránd University, in cooperation with Bédé Bagdi Better with You, prepared this year the Map of Happiness of Hungary. The survey, conducted in 2019-20, surveyed 7,863 women and men ages 17 to 92 living in 962 settlements. Among the county seats, Székesfehérvár became the happiest city, while Kaposvár finished at the bottom of the standings. According to the study, people living in small settlements are significantly happier than urban dwellers. The level of happiness of those who live in Budapest is below the average for the Hungarian population.
Many were left in the lurch
As a result of the “city boom”, we went from 344 cities in 1990 to 346 in 2013. According to 2019 data, 102 cities have a population of less than five thousand! And the number of cities below ten thousand is 202. This means that only 144 of the 346 cities are inhabited by more than ten thousand.
The Orbán government after 2010
he was satisfied with the proliferation of dwarf peoples and applied the brakes.
Adjusted the government decree governing the declaration of a city in two steps. The acquisition linked the acquisition of urban status to measurable demographic, institutional and infrastructure parameters. In 2015, it was also established as a condition that to win the title, the population must reach 10,000, with a constant population growth during the previous five years.
The ominous decree set the sewer rate at a minimum of 60 percent, while the proportion of paved inland roads was 90 percent. According to the standard of the legislators, the average level of urban development has been reached in particular by a municipality with an institution of primary and secondary education, a local police station or police station, a professional or municipal fire department, primary health care, a certification school or a multipurpose sports hall.
The tightening has achieved its goal:
In 2015, none of the 23 applicant municipalities and large villages was screened.
Among other things, various resorts on Lake Balaton (Balatonszárszó, Csopak, Révfülöp, Tihany), Bőcs, famous for its brewery, Abasár and Etyek, famous for its winery, but Recsk, which became famous for its old labor camp forced, remained in Hoppo.
The procedure for declaring a city is determined by municipal law. Applications are evaluated in advance by a committee of experts before they are placed on the table of the minister responsible for overseeing the legality of local governments (the minister in charge of the Prime Minister’s Office). The government will make a proposal to the President of the Republic before June 30 of each non-electoral year, who will decide to declare the city before July 31. As far as we know, the minister in charge of the Prime Minister’s Office, as in 2017, did not submit a proposal to the Head of State this year to grant a city title.
The focus is on county rights
The most livable cities in Hungary in 2019
Last December, the Otthon Centrum produced its own “quality of life indicator” for the fourth time, examining cities with a population of more than 20,000. According to György Kosztolánczy, CEO of the company, the values of Veszprém and Eger were the best in rural settlements (67-61 percent). The regional centers were very similar: Győr and Szeged (54%) and Debrecen (53%) hardly lagged behind the values of Székesfehérvár and Pécs (55%). The research also covered settlements in the agglomeration, where the Budaörs and Szentendre values are the best (57-55 percent). The two settlements stood out among the other cities in terms of the number of immigrants, which confirms the previous data, according to which the settlements near the capital of the county of Pest achieved the highest migration gain in recent years.
The focus of the Orbán government’s settlement development policy is not on the towns that move into city leadership. Coincidentally, in the year of the brutal hardening of the government decree that regulates the territorial ordering procedure, in 2015 the Modern Cities Program was launched, which
it unambiguously focused on the 23 cities with county status.
Within the framework of the program, in Békéscsaba, Debrecen, Dunaújváros, Eger, Érd, Győr, Hódmezővásárhely, Kaposvár, Kecskemét, Miskolc, Nagykanizsa, Nyíregyháza, Pécs, Salgótarján, Soprzékesheged, culture, sports, Sárno and other developments.
Finance Minister Mihály Varga announced at the County Cities with Rights General Assembly in mid-summer that the Modern Cities Program supports a total of 270 projects, with a total value of HUF 4 billion. The affected local governments have so far received more than 1.8 billion guilders in national and EU support. The program will continue in 2021 with an additional budget of 50 billion.
Small Town Development Proposal Package
Following the Modern Cities Program, in 2019 the government also launched the Hungarian Villages Program for settlements with fewer than 5,000 inhabitants. In the first year, it was possible to request 150 billion HUF. The program is also supported by the interest association of more than half of Hungarian local governments, the National Association of Local Governments (TÖOSZ). Ferenc Gyergyák, the organization’s general secretary, told Index:
the development of small towns has taken a back seat in many respects along with the two programs. Therefore, in 2020-2024, I would like the Hungarian Small Towns Program to be developed and launched within the EU developments for settlements with a population between 5,000 and 20,000 inhabitants.
He added that TÖOSZ, inspired by the Hungarian Peoples Program, is committed to working together with the government and
A package of proposals will be developed and delivered to the government in the fall.
Regarding the financing of the settlements, he also mentioned that almost 2,300 of the 3,178 settlements in the country had no tax income other than the automobile tax. The part of the car tax deducted in 2020 and 2021 should be received again by the municipalities from 2022, according to the Secretary General.
Top Image: Prime Minister Viktor Orbán will deliver a speech at the 51st General Assembly of the Association of Cities with County Rights at Veszprém Mayor’s Office on February 8, 2018. MTI photo: Szilárd Koszticsák
[ad_2]