
[ad_1]
In May 2017, the planet was ravaged by a little-known cyber threat as of that date: a ransomware dubbed WannaCry, which managed to affect computers in around 150 countries, including Chile.
He Data hijacking it’s a kind of cyber attack whose function is to enter a network of computers, capture the information that is in it and then demand a ransom for their release.
It is the fastest growing type of attack in the world, due to the efficiency it generates in these virtual hijackers, and the profits they generate. Many organizations simply pay the ransom, especially when it comes to critical attacks.
The attack seems to be very sophisticated, but its mechanism is quite crude. It is estimated that 56% of attacks arrive through email, either with a downloadable and executable file (of the type “see the last photo of Angelina Jolie”) or a link to a site (“click here to get free money”) From which the malicious program is downloaded.
This is when The pirate Encrypt the most important files or folders and start trading. Through anonymous communication tools, the hijacker reports that the computer has been taken hostage and that to free it, you will need to pay a deposit.
“Ransomware in general does not steal or access the information content, but rather blocks access to it,” he explains. Cecilia Pastorino, IT security specialist at ESET Latin America.
The expert adds that since most companies work with shared information networks, ”An infection can spread rapidly through the network, infecting not only employee workstations, but also the company’s servers and databases, where critical and sensitive information is often housed ”.
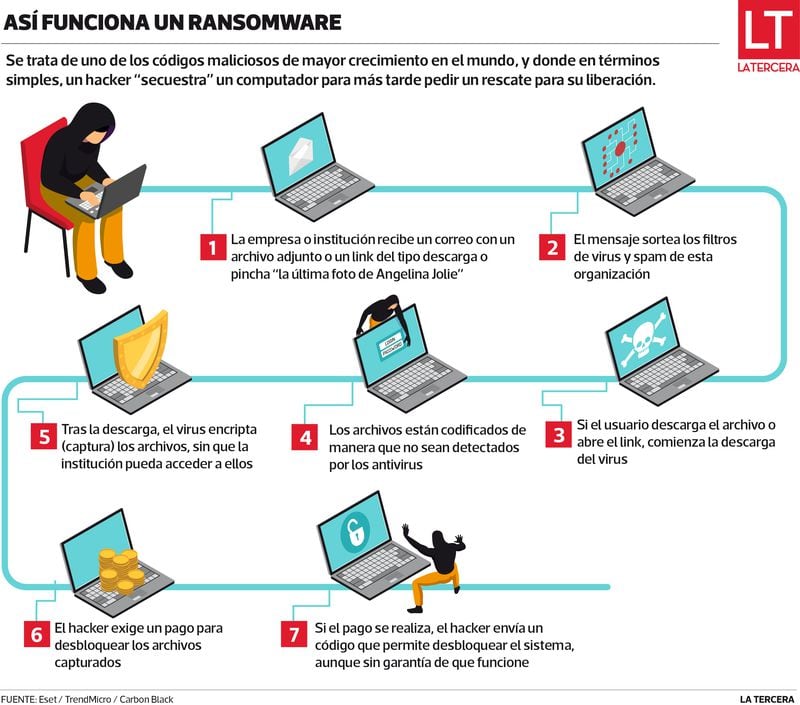
Just like a real hostage taking, it even offers to release some files as proof of its power. After that, the lawsuits begin: if the required sum is not paid in an amount of time, access to those files will be lost forever.
Gabriel Jefferies, a graduate in Communication Sciences from the U. Mayor, says that this rescue, it is generally charged by means of electronic currencies or bitcoins.
“All financial institutions they are a very attractive target for this type of attackThat is why they are always challenged to be constantly with the highest levels of security, looking for gaps, security flaws where opportunities could eventually be generated to deploy an attack of these characteristics ”, he explains.
Dmitry Bestuzhev, Director of the Global Research and Analysis Team from Kaspersky in Latin America, explains that there is a type of ransomware exclusively for commercial or governmental entities, called “Sodinokibi”. “It is one of the most fearsome, because has been very successful in targeting different victims globally. And it is not the first time it has attacked Chile, it is the same malware family that attacked another company a week ago ”.
Say what there is no reason to believe that this will stop, rather companies should prepare to do something different, “Because the ways to defend oneself up to now have not worked. If they follow the same defense techniques, don’t expect things to improve. “
Pablo Nadeau, sales director of the security company McAfee, states that these types of attacks encrypt (hijack) files on a system. “This ransomware not only encrypts files, but also steals system information and threatens the user with paying the ransom. “
In relation to advice for company users, Nadeau recommends “Do not open document attachments unless specifically requested by the sender. Please view the email header or send a separate email to validate the sender before opening attachments. “
According to the 24th edition of Annual Safety Report (ISTR) prepared by the cybersecurity company Symantec, which analyzes 157 countries and details the main findings around global threats, trends and motivations of cyber criminals, Chile was ranked fifth among countries most prone to cyber attacks, after Argentina in fourth place, Venezuela in third place, Mexico in second and Brazil in first place.
The report is based on eight metrics that represent the main sources of threats. These are: malware, spam, phishing hosts, bots, network attacks, web attacks, ransomware, and cryptojacking. Each threat vector is weighted equally for risk when analyzing the data.
[ad_2]