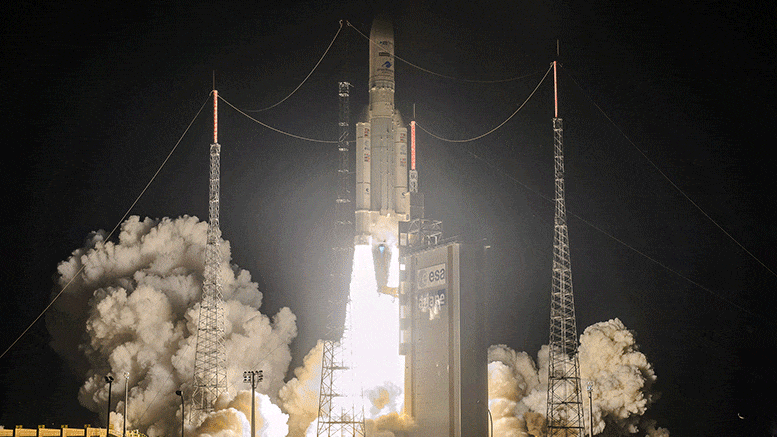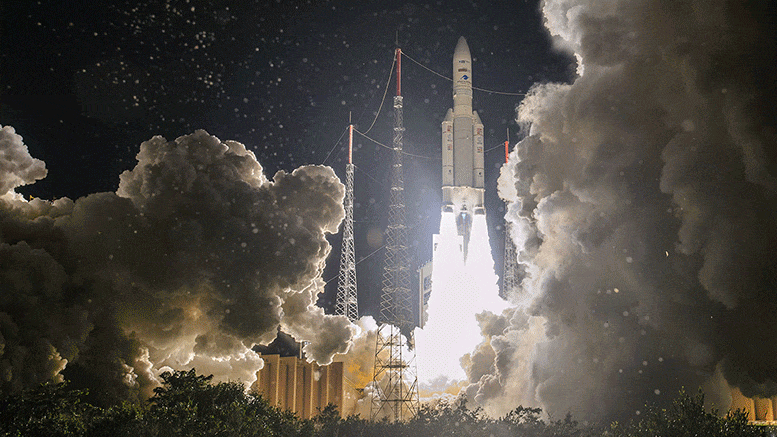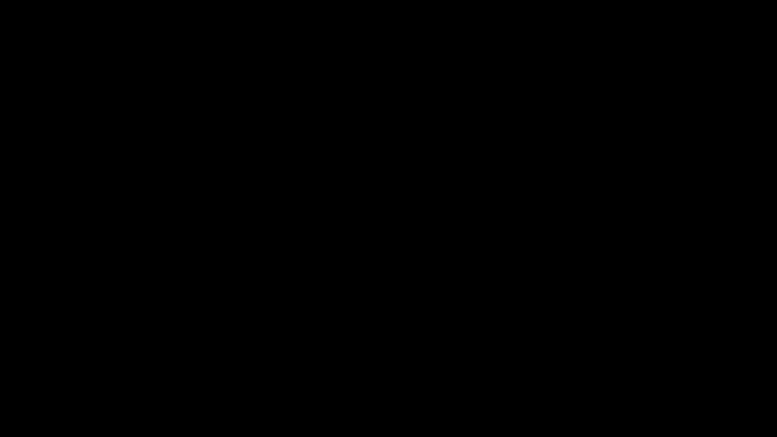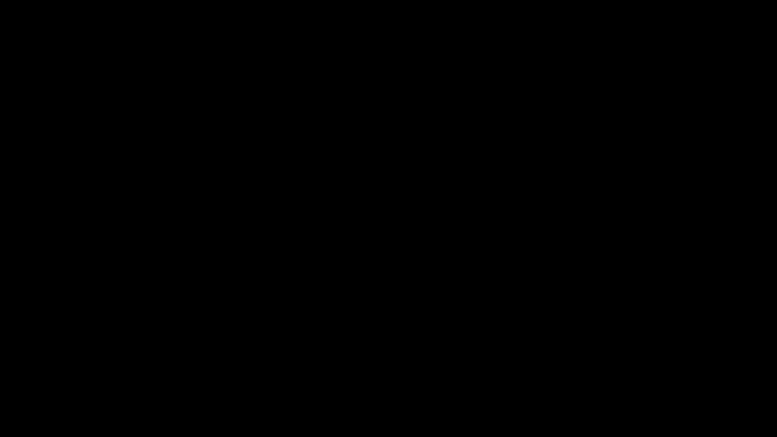

On 15 August 2020, Ariane took flight 5 VA253 from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana and delivered two telecom satellites Galaxy-30 and BSAT-4B, and the Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV-2), in their planned transfer lanes.
European Ariane 5 has delivered two telecom satellites Galaxy-30 and BSAT-4B, and the Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV-2) in its planned transfer lanes. There are also four notable upgrades to the starter car.
Arianespace announced lift at 23:04 BST (00:04 CEST, 19:04 local time) this evening from the European Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, for a mission lasting approximately 47 minutes.
Galaxy-30, with a lance weight of 3298 kg, was the first to be released after about 27 minutes. The 2875 kg MEV-2, also housed in the upper cage of the chain, was released about seven minutes later.

After a series of burns controlled by Ariane’s computer, the Sylda structure was enclosed by the 3530 kg BSAT-4B then jettison. BSAT-4B was released about thirteen minutes after MEV-2 in its own transmission orbit.
Galaxy-30 is owned by Intelsat and will deliver high-performance broadcast content, including ultra-high definition and over-the-top streaming media, while also supporting broadband, mobility and enterprise networking solutions. It has a design life of 15 years.

The MEV-2 is owned by Northrop Grumman and will be used for satellite orbit savings.
BSAT-4B, owned and operated by Japan’s Broadcasting Satellite System Corporation, will provide high definition direct television services across the Japanese archipelago. The satellite has a design life of at least 15 years.
The performance requested for this launch was about 10,468 kg. The satellites weighed a total of about 9703 kg, with custom load loads and supporting structures that make up the rest.
This is the first launch following the resumption of operational activities at the European Spaceport in French Guiana, following the suspension of launch campaigns launched on 16 March 2020 due to COVID-19 measures.
Also on this flight, there are four new technical modifications to Ariane 5.
New charging technology called Kassav is the first version of an autonomous tracking kit developed by CNES in collaboration with ArianeGroup. Regardless of the launch car’s actions, Kassav uses dedicated telemetry to send real-time information about Ariane’s position and speed to the Flight Safety team at Europe’s Spaceport.
CNES funded the development of the kit and oversaw safe use, while ESA funded the installation and oversaw the launch vehicle. Cassava will now be used on all Ariane 5 and Ariane 6 flights.

A further modification of the fairing of Ariane 5 will minimize depression at divorce, as this two-piece nose cone is jettisoned away from the launch car in space. Manufactured by RUAG Space Switzerland, the fairing protects the loadloads of customers against the acoustic, thermal and aerodynamic stresses during takeoff. New hardware ensures that vent ports around the base of the fairing remain fully open on their way to space, allowing the pressure in the fairing to equalize before opening and falling away from the rocket.
This change is part of the preparations for the launch of the NASA / ESA / CSA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) set for October 2021. These changes reduce the concerns about residual air pressure in the JWST sunscreen membranes’ teams. high voltage can cause at the time of separation of fairing, potentially sensitive components damage.

The car equipment bay (VEB), the ‘brain’ of the starter car, which controls the avionics, the guidance system and other important components of interest with the upper stage, is made 85 kg lighter on the central cone by the use of new materials and removal of metallic interfaces. This modification increases the total capacity of Ariane 5 to geostationary transfer orbit to 10 300 kg.
During the re-arrangement of the cone, the membrane separating the VEB and the upper stage were also made a few kilograms lighter with innovative production technologies. This membrane will continue to be used on all Ariane 5 flights and also included in the upcoming Ariane 6.
Flight VA253 was the 109th Ariane 5 mission.

Artist’s view of the James Webb Space Telescope on an Ariane 5 launcher. Credit: ESA – D. Ducros
About Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is operated by Arianespace at the Spaceport of Europe. It is capable of carrying load loads exceeding 10 tons to geostationary transmission orbit and carrying more than 20 tons in low-earth orbit. The performance is perfectly complemented by that of the Europe Vega light lift launched car, and Soyuz.
Europe’s next-generation Ariane 6 rocket will eventually replace Ariane 5. Available in two versions, it will be able to assign a wide range of missions to each job.
Images: ESA / CNES / Arianespace